Figure 2. Molecular analysis of transcripts resulting from TINF2 mutations.
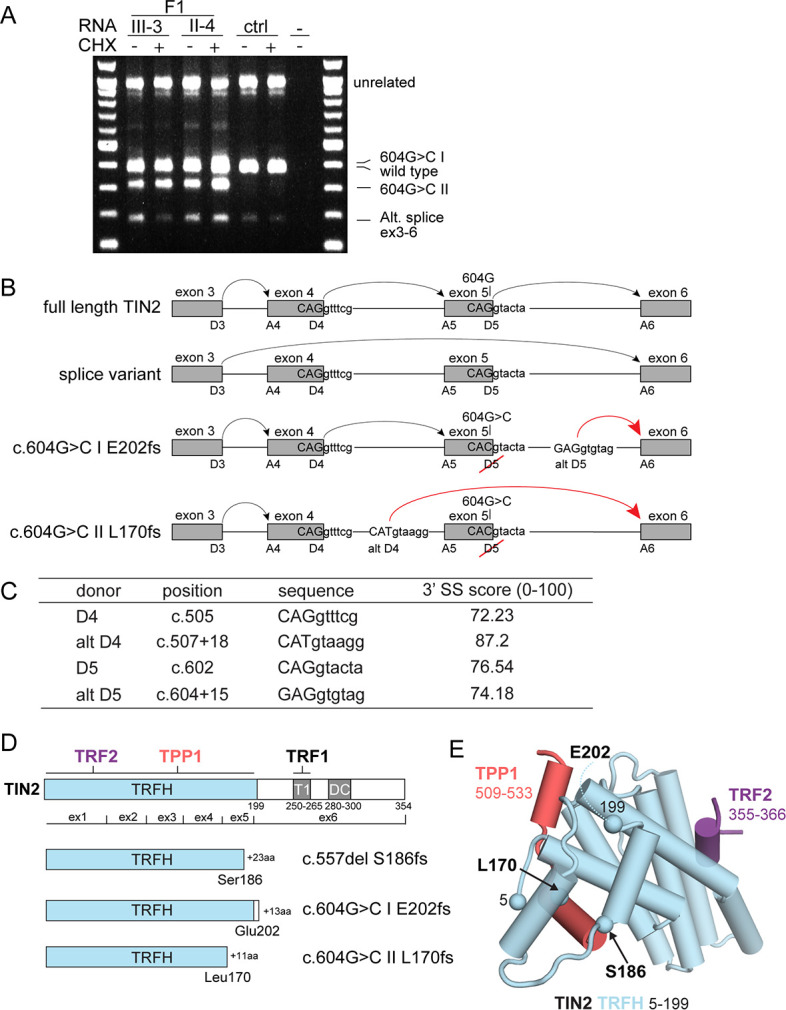
(A) Transcript analysis in peripheral blood lymphocytes (with and without cycloheximide treatment, CHX) from patients with the c.604G > C TINF2 mutation (F1:III-3 and F1:II-4; see Figure 1A) and a control individual. RT-PCR products were analyzed by Sanger sequencing. Wild-type full-length TIN2 mRNA, an alternative splice form found in wild-type cells (alt. splice exons 3–6) and mutant allele transcripts (604G > C I and 604G > C II) are indicated. Transcript 604G > C I was identified in heterozygous +/c.604G > C and homozygous c.604G > C RPE1 cells. (B) Schematic showing the splicing of exons 3–6 for full-length wild-type TINF2, the alternative splice variant (exons 3–6), and the aberrant splicing occurring in cells with c.604G > C mutations. Alt D4 and alt D5 indicate alternative splice donor sites. (C) Comparison of the consensus score of alternative splice donor sites alt D4 and alt D5 to splice donors D4 and D5 (as calculated by Human Splicing Finder www.umd.be). (D) Schematic of wild-type TIN2, and the predicted truncations resulting from expression of c.557del p.(S186fs), c.604G > C I p.(E202fs), and c.604G > C II p.(L170fs). Exon boundaries and the regions involved in TIN2 interactions with TRF1, TRF2, and TPP1 and the DC patch are indicated. (E) Structure of the TIN2 TRFH domain (PDB ID: 5xyf; Hu et al., 2017) with the amino acids at the truncation points highlighted. Peptides from TPP1 and TRF2 that interact with the TRFH domain are shown in the structure.
