Figure 4.
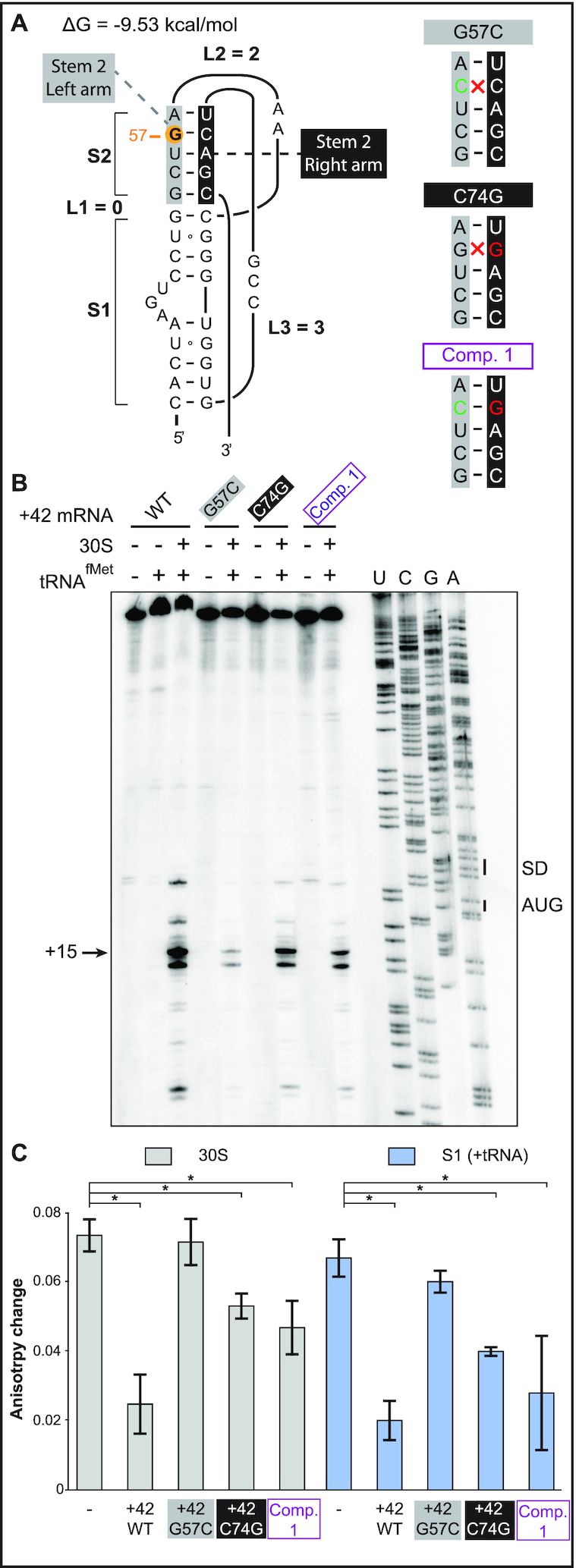
Rescue of 30S-IC formation and ribosome binding by the double-mutant G57C / C74G. (A) (Left) Secondary structure model of the 5′-end pseudoknot in wild-type +42 tisB mRNA. Nucleotides forming stem 2 are indicated in grey and black boxes (left and right arms of the helix, respectively), and the G57 is highlighted by an orange circle. (Right) Representation of the stem 2 helix with the G57C base substitution (green base), C74G (red) and the double compensatory mutant Comp. 1 (purple). Disruption of Watson-Crick base pairing is indicated (red cross). (B) Toeprint assays on +42 tisB mRNA (WT) and mutated variants G57C, C74G, and the compensatory double mutant G57C/C74G (Comp. 1). The position of the toeprint signal at +15 is indicated. (C) Fluorescence anisotropy change of 5′-end FAM-labeled +42 tisB mRNA was conducted as in Figure 2B. Complexes were competed with a 50-fold molar excess of wild-type +42 tisB mRNA or the corresponding G57C, C74G, and G57C/C74G (Comp. 1) variants. *P-value < 0.05 (triplicate)
