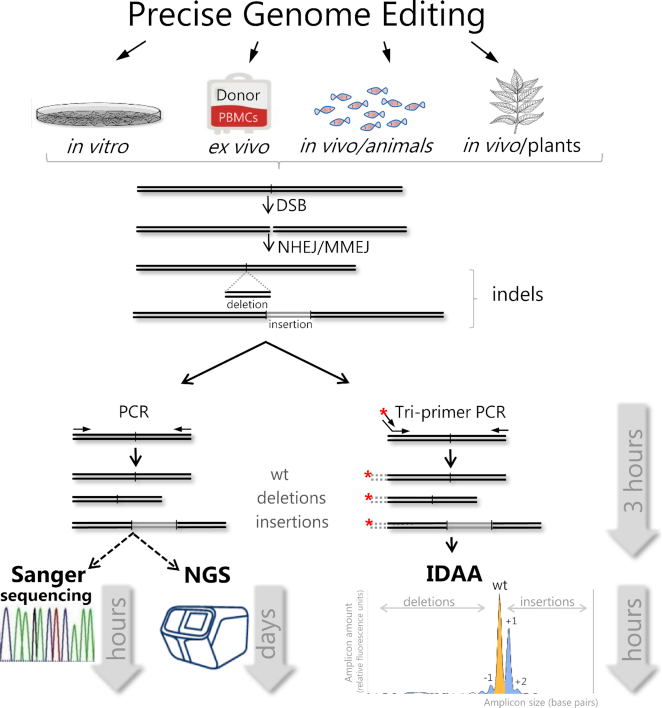
Figure 4.
Schematic outline of indel profiling workflows of Sanger sequence decomposition (TIDE/ICE), NGS and IDAA and sample-to-data time required. At the top, examples of genome editing applications, where these indel detection methods have been used. The primary outcome is a DNA double-strand break (DSB) followed by NHEJ/MMEJ-mediated indel formation induced by PNs. The targeted region is amplified by standard PCR or fluorophore tri-primer PCR. At bottom panels, amplicons can be gel purified, followed by analysis by Sanger sequence deconvolution using TIDE/ICE software or by NGS. Alternatively, tri-primer, fluorophore-labelled amplicons can be directly subjected to IDAA by capillary electrophoretic fragment analysis, followed by indel analysis. Cas9 targeting of human ST6GALNAC1 promoter illustrates an IDAA profile generated by ProfileIT software with typical size distribution and frequencies of WT, out-of-frame and in-frame amplicons (indels) represented by peaks colour-coded in yellow, blue and white, respectively.