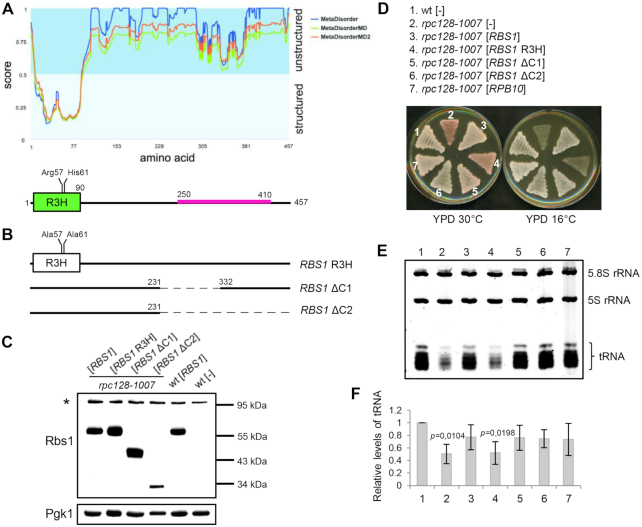
Figure 1.
The R3H domain is essential for the function of Rbs1 protein in Pol III assembly. (A) Predicted disorder of Rbs1 protein according to Metadisorder server (30). Localization of the R3H domain (green) and the prionogenic sequence (pink) is shown below. (B) Schematic presentation of modified versions of RBS1 that were constructed on corresponding plasmids: [RBS1 R3H], [RBS1 ΔC1] and [RBS1 ΔC2]. See the Materials and Methods section for details. (C-F) Examination of transformants of control strain (wild type [wt]) and rpc128-1007 mutant with plasmids that encoded modified versions of Rbs1 protein, [RBS1] and [RPB10] control plasmids, and the empty vector [–]. (C) The modified versions of Rbs1 protein were efficiently expressed. Yeast cells were analyzed by western blot. Antibody specific for Rbs1 detects only overproduced protein. Determination of Pgk1 levels served as loading control. (D) Inactivation of the R3H domain prevented genetic suppression of the Pol III assembly mutant. Cells that were grown on an SC-ura plate were replicated on YPD plates and incubated for 3 days at the respective temperatures. (E) Inactivation of the R3H domain prevented the correction of low tRNA levels in the Pol III assembly mutant. Small RNA species were separated on a 7 M urea–6% polyacrylamide gel using equal amounts of RNA per lane (5 μg) and stained with ethidium bromide. (F) Bands corresponding to total tRNAs were quantified. Bars represent tRNA levels normalized to 5.8S rRNA which served as loading control. Standard deviations were estimated on the basis of three independent experiments. The P value calculated for ratio of tRNAs (rpc128-1007[-]/wt[-], rpc128-1007[RBS1R3H]/wt[-] showed statistical significance (P < 0.02). P values were calculated using a two-tailed t-test.