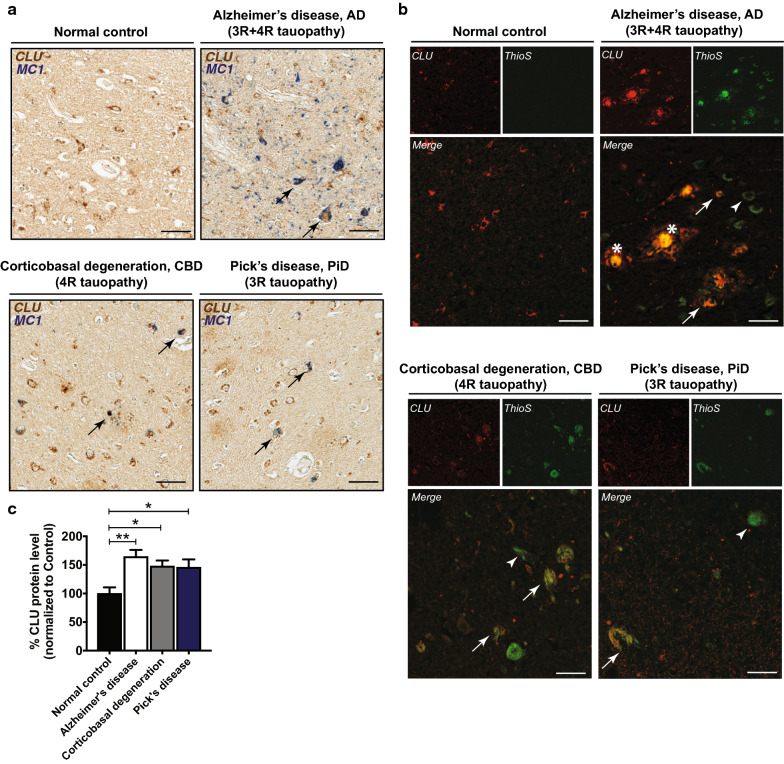
Fig. 1.
Clusterin co-localizes with tau deposits and is upregulated in human tauopathies. a Human brain tissues representing normal control, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and the primary tauopathies Pick’s disease (PiD) and corticobasal degeneration (CBD). Co-localization of CLU (brown) with tau deposits, marked by MC-1 labeling (blue). Scale bar, 100 μm. b Arrows indicate co-localization of CLU (red) with mature tau tangles labeled by thioflavine-S staining (green). Arrowheads show tau tangles without CLU co-localization. Asterisks represent amyloid plaques. Scale bar, 100 μm. c Biochemical evaluation of the total CLU protein levels in the cortical region of human tauopathies. N = 10–15 cases/group. Data presented as mean ± S.E.M. and analyzed with one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01