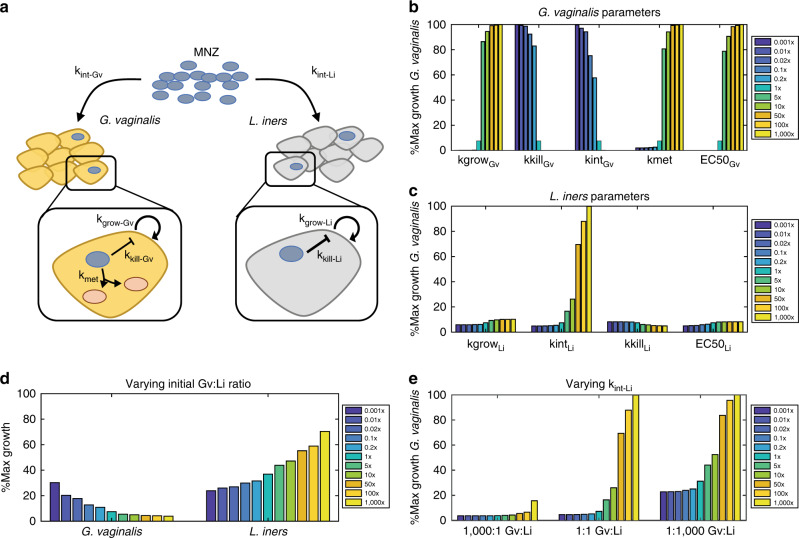
Fig. 1. Model schematic for bacterial growth dynamics in BV with MNZ treatment.
a MNZ is internalized by both G. vaginalis (Gv) and L. iners (Li) at rates kint-GV and kint-LI, cells are proliferating at kgrow-GV and kgrow-LI and MNZ inhibits growth by kkill-GV and kkill-LI. For Gv, a potential mechanism of MNZ resistance is the bacterial-mediated interactions to the drug leading to the formation of metabolites (kmet). b Sensitivity of Gv growth with 500 μg/ml MNZ when parameters directly related to Gv growth are varied 0.001× to 1000× baseline values. Percent maximal growth refers to the final cell count compared to the carrying capacity of the culture, or the maximum cell density the unperturbed culture can reach at 48 h based on initial cell density. c Sensitivity of Gv growth with 500 μg/ml MNZ when parameters related to Li survival are varied 0.001× to 1000× baseline values. d Percent maximal growth of Gv (left) and Li (right) when the initial ratio of Gv to Li is varied with 500 μg/ml MNZ treatment. e Percent maximal growth of Gv when MNZ internalization rate of Li is varied at three different population compositions with 500 μg/ml MNZ treatment.