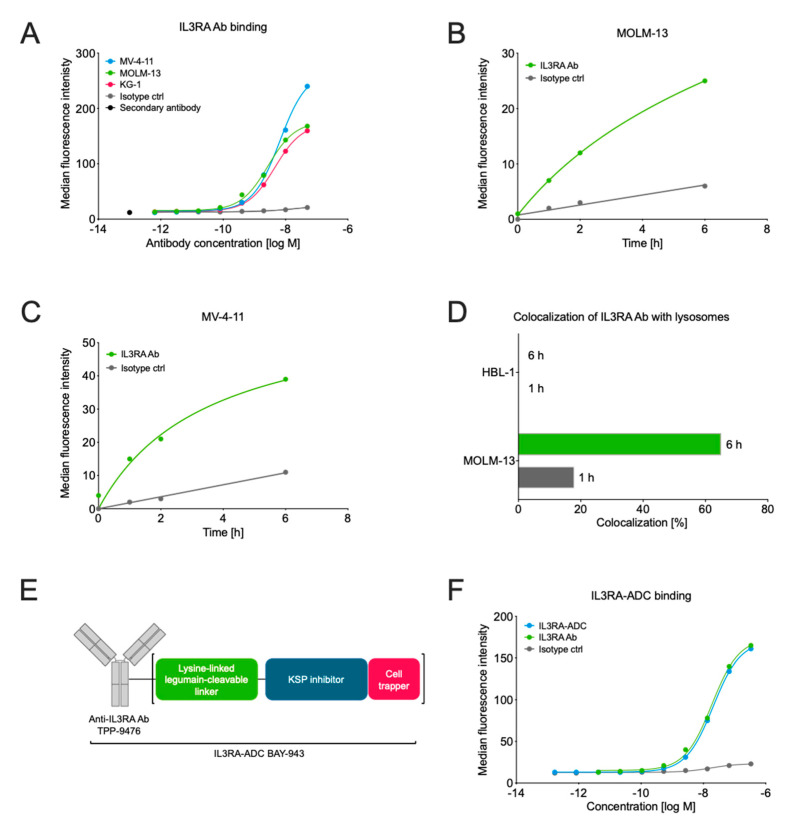
Figure 1.
Characterization of the interleukin 3 receptor subunit alpha (IL3RA) antibody TPP-9476 and schematic representation of the IL3RA antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) BAY-943. (A) The binding of the IL3RA-targeting antibody (IL3RA Ab) TPP-9476 to IL3RA-positive hematologic cell lines as determined by flow cytometry. The obtained EC50 values were 2.73 × 10−9 M for MOLM-13, 6.53 × 10−9 M for MV-4-11, and 4.54 × 10−9 M for KG-1 cells. (B,C) The internalization of the IL3RA Ab TPP-9476 and an isotype control antibody into IL3RA-positive MOLM-13 (B) and MV-4-11 (C) cells as determined by flow cytometry-based imaging. (D) The colocalization of the IL3RA Ab TPP-9476 in lysosomes in the IL3RA-positive MOLM-13 and IL3RA-negative HBL-1 cells. (E) Schematic representation of the IL3RA-ADC BAY-943. TPP-9476 represents the IL3RA-Ab. The “cell trapper” functionality indicates a non-cell-permeable payload metabolite that enables maximal retention in target cells after cleavage. (F) The binding of the IL3RA-ADC BAY-943 to IL3RA-positive MOLM-13 cells as determined by flow cytometry. The obtained EC50 values were 20.4 × 10−9 M for ILRA3A-ADC and 18.7 × 10−9 M for ILRA3A Ab, respectively.