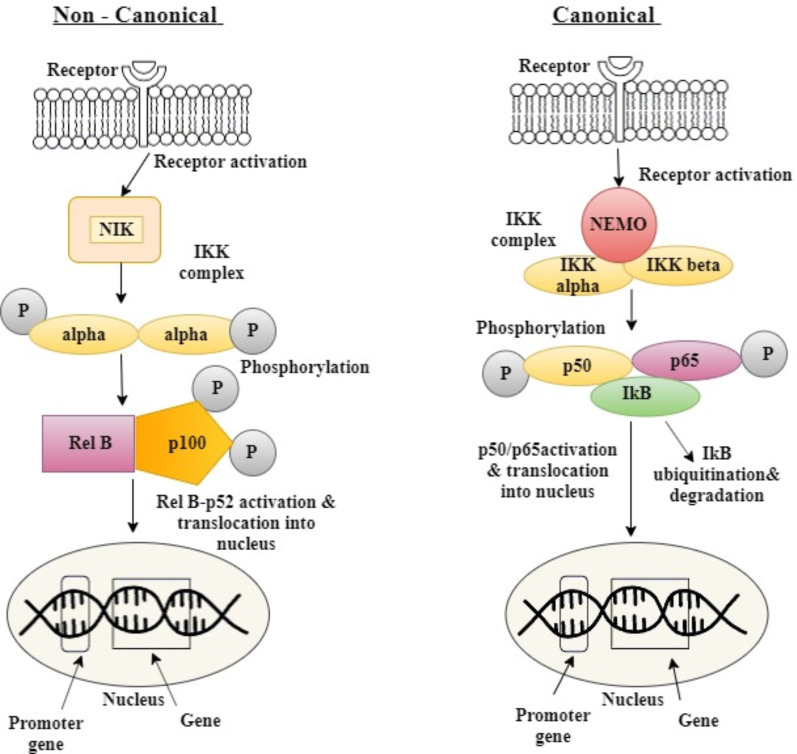
Fig. (2).
Canonical/ Classical pathway and the Non- Canonical/ Alternative pathway of NF-KB. In the canonical pathway, the toll-like receptor gets activated by large stimuli and binding of ligand and recruiting the activation of IKB complex (IKK) complex, and then phosphorylates inhibitory enzyme (IKB) getting degraded by ubiquination. Further, the activated NF-KB complex (p50/p65) translocates into the nucleus to transcribe genes. In Non-canonical/alternative pathway, the activation of NF-KB inducing kinase (NIK) in response to very small stimuli (lymphotoxin B, B cell-activating factor) carries the intracellular signaling. The NIK phosphorylates the 2 IKK –alpha subunits phosphorylating p100, further activating heterodimer p52/RelB complex to translocate into the nucleus. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).