Figure 2 |.
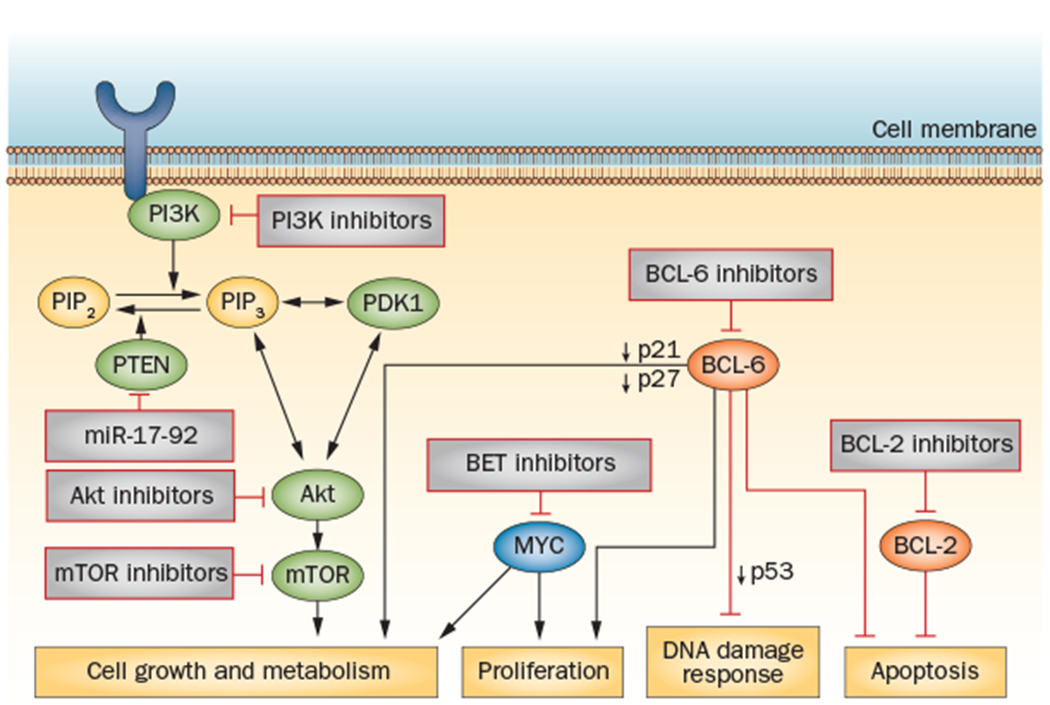
The key signalling pathways implicated in GCB DLBCL with targeted novel agents in clinical development. Loss of PTEN expression is found in 55% of cases of GCB DLBCL, resulting in activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway;53 small-molecule inhibitors of this pathway can be effective in cases of GCB DLBCL with decreased PTEN expression. BCL-6 is frequently activated in GCB DLBCL; BCL6 deregulation results in enhanced tumour proliferation via decreased expression of the cell-cycle checkpoint proteins p21 and p27, impaired DNA damage response through decreased p53 expression, impaired cellular metabolism and resistance to apoptosis.70 Inhibitors that target key co-repressor proteins of BCL-6 are in preclinical development.72 In normal B cells, BCL-6 suppresses transcription of the MYC oncogene; in 10–15% cases of DLBCL this mechanism is bypassed through MYC oncogene translocation, resulting in uncontrolled cellular metabolism and growth.31 BET bromodomain inhibitors are in early clinical development and represent a novel strategy of epigenetic regulation of MYC-driven tumours.143 BCL2 translocations are observed in up to 35% of GCB DLBCL cases, resulting in inhibition of apoptosis.63 Inhibitors of BCL-2, such as ABT-263, have demonstrated early clinical activity in B-cell malignancies.65 Abbreviations: BCL-2, apoptosis regulator Bcl-2; BCL-6, B-cell lymphoma 6; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; GCB, germinal centre B-cell; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
