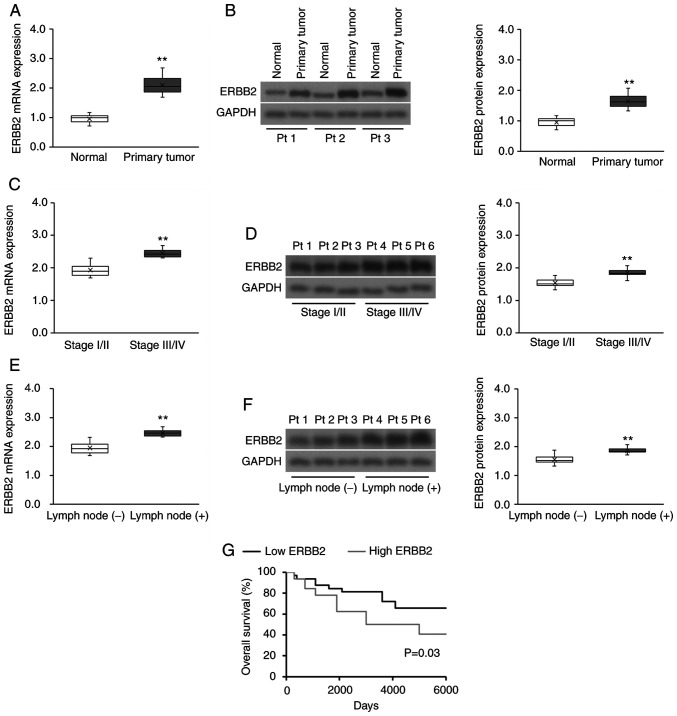
Figure 1.
ERBB2 expression is upregulated in patient-derived cervical cancer tissues and is associated with a poor prognosis. (A) RT-qPCR and (B) WB analysis of ERBB2 transcript and protein expression, respectively, in patient-derived cervical cancer tissues (n=65) vs. matched healthy cervical tissues (n=65). Data were analyzed via Wilcoxon signed-rank test. (C) RT-qPCR and (D) WB analysis of ERBB2 transcript and protein expression, respectively, in stage I/II vs. stage III/IV patient-derived cervical cancer tissues (n=43 stage I/II; n=22 Stage III/IV). Data were analyzed via Mann-Whitney U test. (E) RT-qPCR and (F) WB analysis of ERBB2 transcript and protein expression, respectively, in lymph node metastatic and non-metastatic patient-derived cervical cancer biopsies [n=46 lymph node (−); n=19 lymph node (+)]. Data were analyzed via Mann-Whitney U test. (G) Survival analysis using the Kaplan-Meier method according to high (above the median) or low (below the median) ERBB2 mRNA expression (n=32 in each cohort). The P-value was calculated using the log-rank test. For purposes of comparison across cohorts, the median ERBB2 mRNA and protein expression levels (normalized to the RT-qPCR housekeeping control and WB loading control GAPDH) in the normal cohort have been set to 1.0. Data in box plots are expressed as the median ± IQRs (boxes) and absolute ranges (whiskers). n=3. **P<0.01. RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; WB, western blotting; ERBB2, Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 2; Pt, patient.