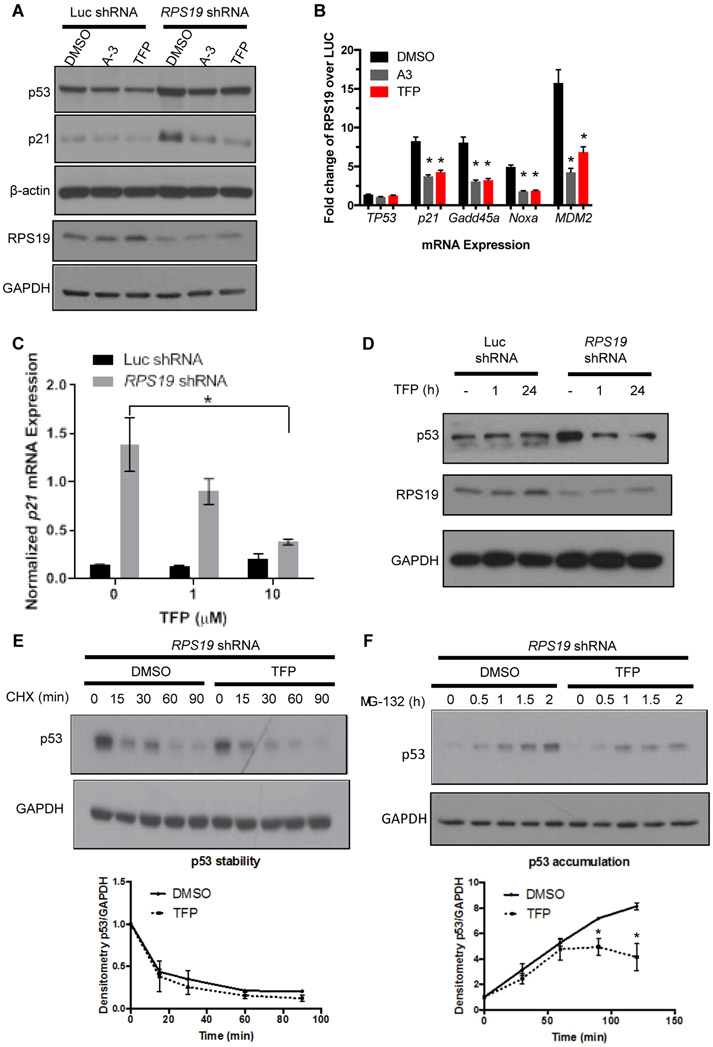
Fig. 2. TFP dose-dependently reduces p53 in RPS19-deficient human cells and primary human hematopoietic progenitors.
A. p53 and p21 protein, as measured by Western blot, in A549 cells with shRNA targeting luciferase or RPS19 and treated with DMSO, 50 μM A-3, or 20 μM TFP.
B. qPCR measuring expression of TP53, P21, GADD45A, NOXA, or MDM2 in A549 cells with shRNA targeting luciferase or RPS19 and treated with DMSO, A-3, or TFP. Student t-test, *p < 0.05 compared to DMSO control.
(C-D) CD34+ cells were transduced with RPS19 or control shRNA and selected for successfully transduced GFP+ cells.
C. qPCR measuring p21 mRNA in CD34+ cells treated with increasing doses of TFP. Student t-test, *p < 0.05.
D. Western blot measuring RPS19 and p53 proteins in CD34+ cells treated for increasing lengths of time with 10 μM TFP.
(E-F) CD34+ cells were infected with RPS19 shRNA and selected for GFP+ successfully transduced cells by FACS. Western blots of p53 and GAPDH were quantified by densitometry.
E. Cells were pre-treated with TFP for 15-30 minutes before treatment with 10 μM CHX for increasing lengths of time before lysates were collected for TP53 and GAPDH protein quantification.
F. Cells were pre-treated with TFP for 2 hours before treatment with 20 μM MG-132 for increasing lengths of time before lysates were collected for TP53 and GAPDH protein quantification. Two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05.