Figure 7. UV Light Induces Oncogenic Tandem Substitutions Found in BRAF.
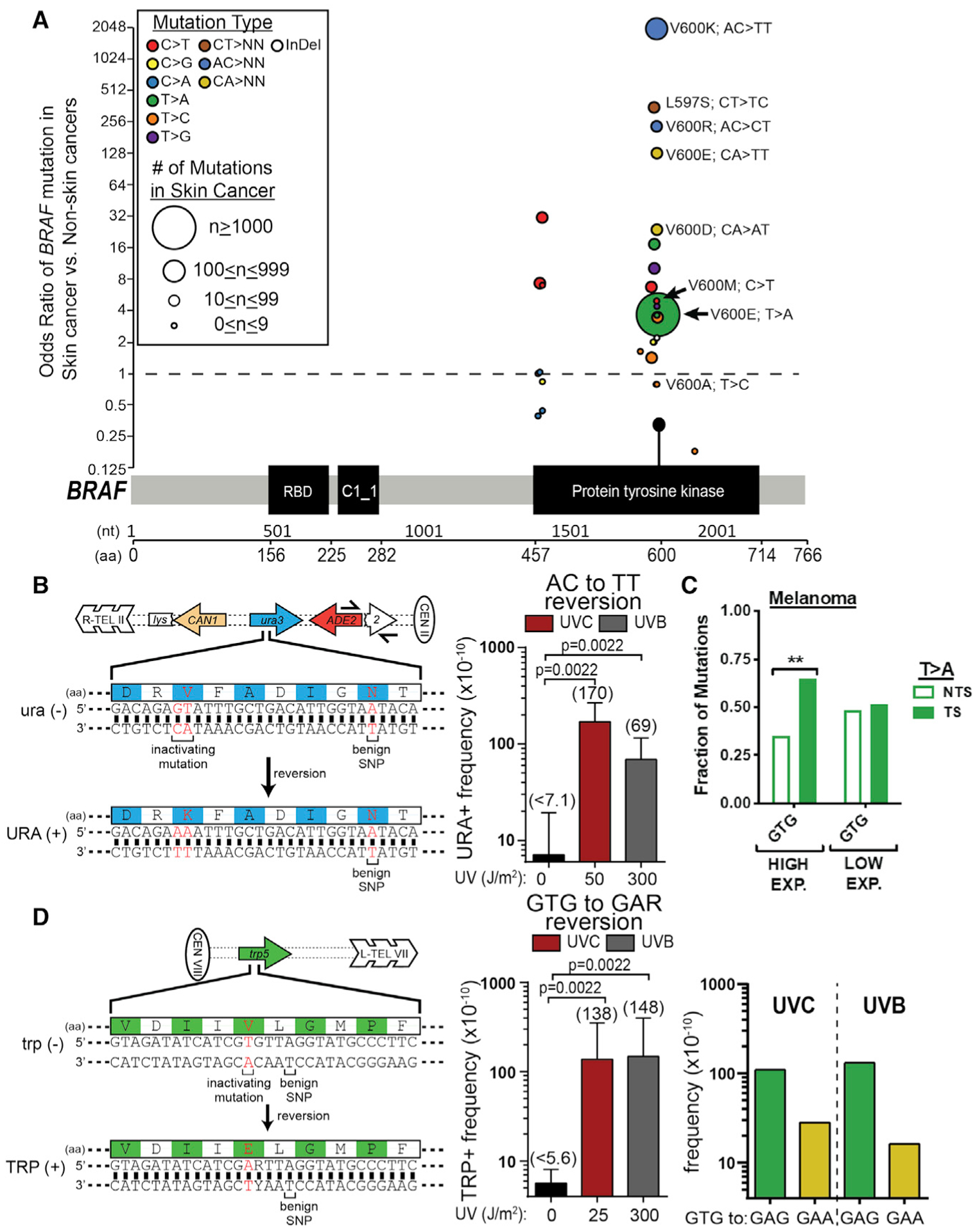
(A) Odds ratio of recurrent substitution mutations (circles) in the BRAF gene in skin cancers relative to non-skin cancers from the COSMIC database (Tate et al., 2019). Each mutation is positioned along the x axis in accordance with its position within the BRAF cDNA. Nucleotide (nt) and amino acid (aa) positions are indicated below the schematic of the BRAF protein domains. Specific substitution types are color coded, and the number of times each recurrent mutation occurs in the dataset is indicated by the size of the circle.
(B) UV light induces AC-to-TT tandem substitutions in yeast. The yeast ura3 K93V reporter is inactive due to an AA-to-GT (red text) substitution at codon 93, resulting in the change of the catalytic lysine (Miller et al., 2001) to valine. Reversion of the ura3 K93V to WT via an AC>TT mutation therefore mimics the BRAF V600K substitution. Median URA+ reversion frequencies were determined from six independent measurements for yeast treated with 0, 50 J/m2 UVC light, or 300 J/m2 UVB light. Error bars indicate ranges. For yeast treated with 0 J/m2 UVC, no URA+ revertants were recovered in any of the six replicates, so a maximum estimated frequency was calculated as if each replicate contained a single URA+ colony. p = 0.0022 by Mann-Whitney ranked sum test.
(C) T>A mutations in a GTG context are significantly enriched on the TS relative to the NTS in highly expressed genes in melanocytes (top quartile), but not in lowly expressed genes (bottom quartile). **p < 0.001.
(D) UV light induces T>A and TG>AA substitutions in a GTG context. Same as (B), except the yeast trp5 E50V reversion reporter was used to mimic the BRAF V600E mutation. Median TRP+ reversion frequencies were determined from six independent measurements for yeast treated with 0, 25 J/m2 UVC light, or 300 J/m2 UVB light. Error bars indicate ranges. p = 0.0022 by Mann-Whitney ranked sum test. Right panel: estimated frequency of T>A (i.e., GTG-to-GAG) and TG>AA (i.e., GTG-to-GAA) mutations in the trp5 reversion assay, based on sequencing of TRP+ revertants.
