Figure 2: Possible Mechanism of Protection of CYP1A Enzymes from Oxidative Stress.
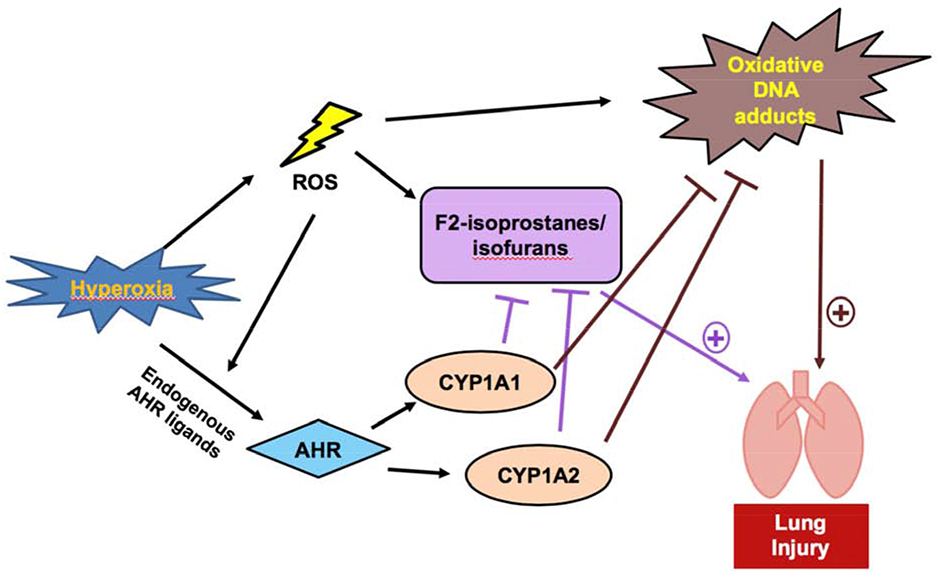
Hyperoxia results in an increase of ROS, which can cause increased levels of lipid hydroperoxide products, such as F2-isoprostanes and isofurans, and DNA adducts [57, 53]. These harmful effects are signs of oxidative stress and result in pulmonary injury [53]. Hyperoxia also upregulates CYP1A enzyme expression via AHR activation [52]. CYP1A enzymes metabolize lipid hydroperoxides and DNA-reactive metabolites, which protects against hyperoxic lung injury [56].
