Figure 4.
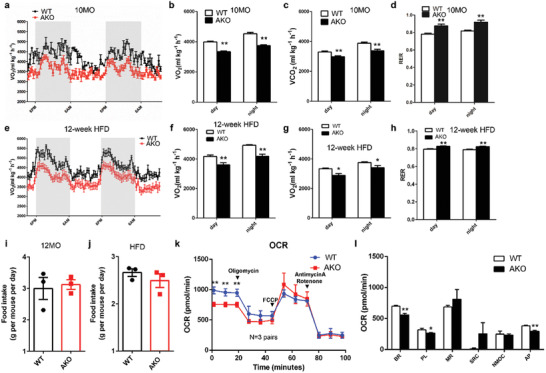
Prmt5AKO mice exhibit lower metabolic rate and lower basal respiration in Prmt5 deficient adipocytes. a) O2 consumption measured by an indirect calorimetry and normalized to lean mass is shown for a 48 h cycle of 10‐month‐old male WT (Prmt5flox/flox) and Prmt5AKO mice. b–d) Average day and night O2 consumption (b) VO2, CO2 production c) VCO2 and d) RER. a–d) n = 5 pairs of 10‐month‐old male mice. e) O2 consumption measured same as above on male WT (Prmt5flox/flox) and Prmt5AKO mice after 12 week of HFD. f–h) Average day and night O2 consumption f) VO2, CO2 production g) VCO2 and h) RER. e–h) n = 6 pairs of male mice after 12 week of HFD. i,j) Food intake of WT (Prmt5flox/flox) and Prmt5AKO mice during i) control‐diet or j) HFD feeding. n = 3 groups of male mice for control‐diet (12‐month‐old) and HFD feeding, respectively. Each dot represents the average food consumption per day of two mice. k,l) Seahorse‐based measurement of oxygen consumption rate (OCR) on white adipocytes differentiated from preadipocytes isolated from iWAT of 8 week old WT (Prmt5flox/flox) and Prmt5AKO mice. k) OCR was measured at basal state and after sequential addition of Oligomycin, FCCP, and Antimycin A/Rotenone to determine the l) Basal Respiration (BR), Maximal Respiration (MR), Spare Respiratory Capacity (SRC), Non‐Mitochondrial Oxygen Consumption (NMOC), and ATP Production (AP), respectively, cells were isolate from the iWAT of n = 4 pairs of male WT (Prmt5flox/flox) and Prmt5AKO mice, measured in five technical replicates. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. (t‐test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).
