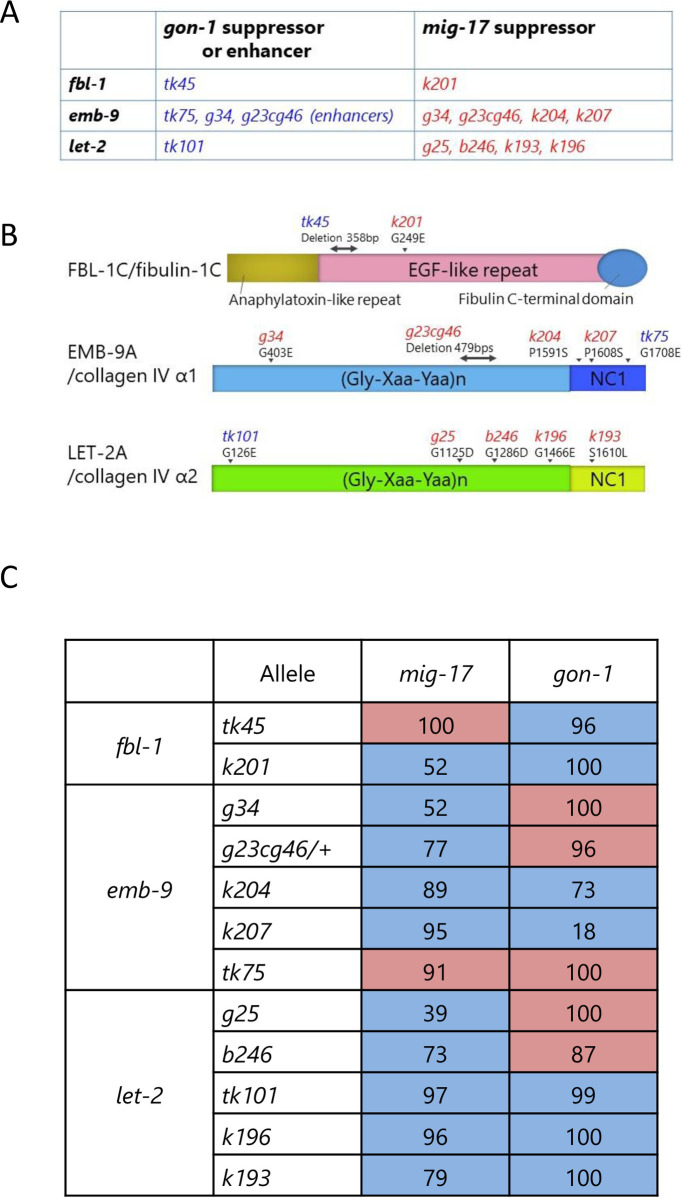
Fig 3. Suppressor and enhancer mutations for gon-1 and mig-17, and summary for swapping experiments of suppressors and enhancers.
A. fbl-1, emb-9 and let-2 alleles that suppress or enhance the gonadal defects of gon-1(e1254) or mig-17(k174). B. Locations of mutations in FBL-1C, EMB-9A and LET-2A proteins. The mutation sites are shown by arrowheads (amino acid substitutions) or bidirectional arrows (deletions). Both fbl-1(tk45) and emb-9(g23cg46) deletions are potential null alleles, as they are expected to introduce termination codons shortly after the deleted region [11, 17]. C. Summary of effects of fbl-1, emb-9 and let-2 alleles on mig-17(k174) and gon-1(e1254) mutants. Blue and red boxes represent suppression and enhancement, respectively. Numeric values representing strength of suppression or enhancement were calculated as follows. Percentages of anterior and posterior gonadal defects were averaged for each strain. Strength of suppression indicates percent recovery of the gonadal defect in double mutants relative to that of the mig-17 or gon-1 single mutants. Strength of enhancement indicates percent decrease of the ratio of non-defective gonads in double mutants relative to that of the mig-17 or gon-1 single mutants.