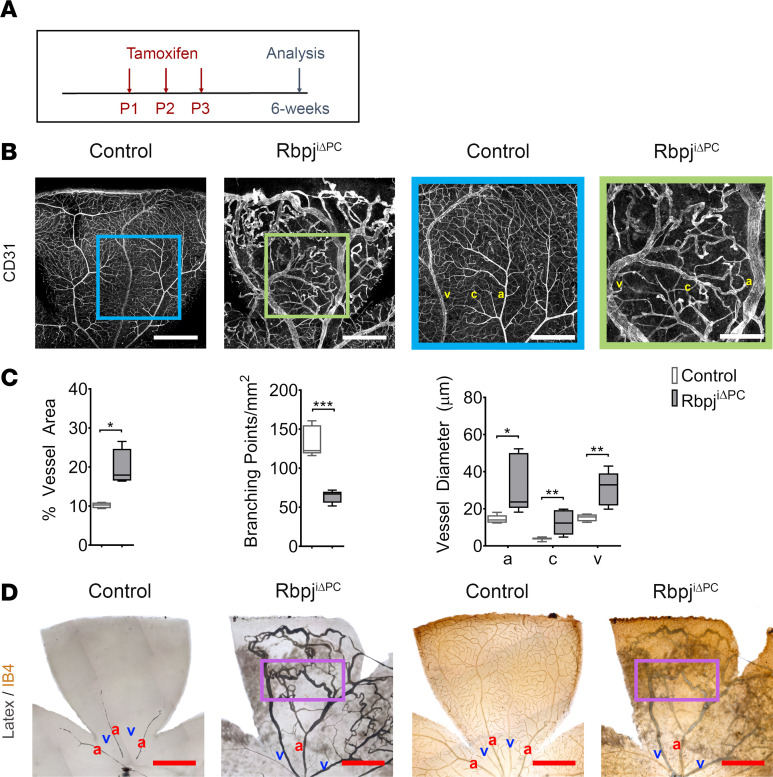
Figure 1. Inhibition of perivascular Notch signaling at birth results in severe AVMs.
(A) Diagram of tamoxifen administration to postnatal control and RbpjiΔPC mice and analysis at 6 weeks. (B) Confocal images showing 6-week retinal vasculature stained with anti-CD31 (white). Right panels show higher magnification of boxed regions highlighting vascular malformations in the retina of RbpjiΔPC mice. Scale bars: 600 μm (left panels) and 300 μm (right panels). (C) Quantification of percentage of vessel area (n = 4), branching points/mm2 (n = 5), and vessel diameter (n = 6–8) in control and RbpjiΔPC mice. (D) Images of the vasculature perfused with blue latex compound. Perfused vessels were subsequently stained with Isolectin B4 (IB4) and detected using HRP streptavidin (n = 3). Boxed region highlights arteriovenous shunt. Scale bars: 600 μm. Box-and-whisker plots show median, minimum, and maximum values. Data were analyzed using unpaired 2-tailed t test with Welch’s correction. a, artery; c, capillary; and v, vein. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.