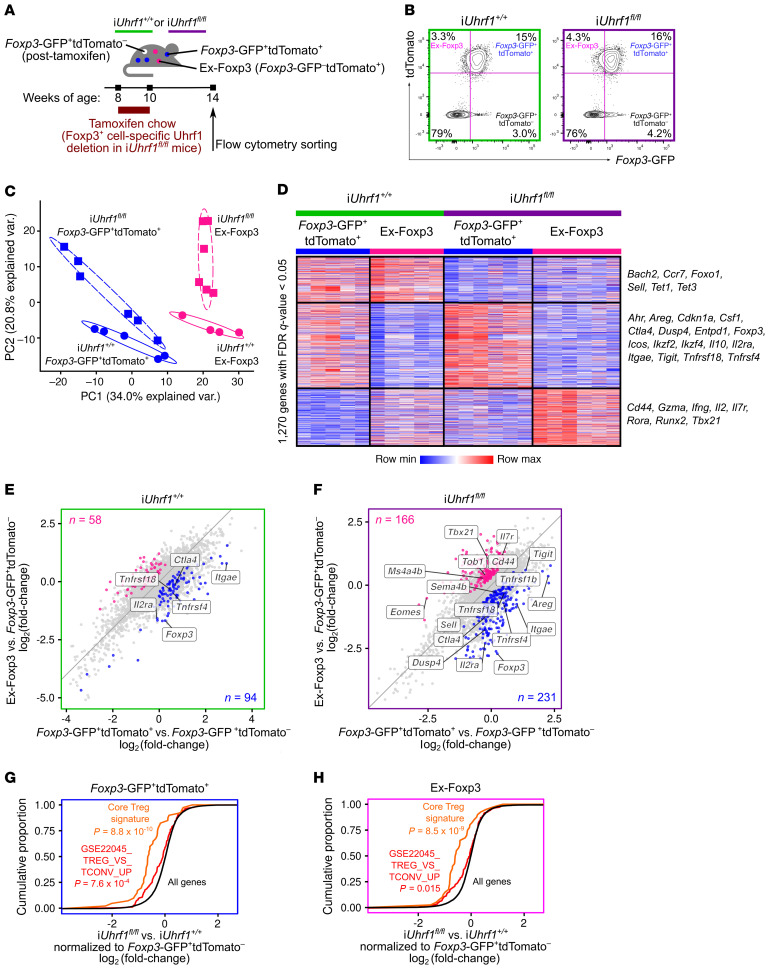
Figure 6. Induction of Uhrf1 deficiency generates ex-Foxp3 cells with distinct inflammatory transcriptional programs.
(A) Schematic of the pulse-chase experimental design. (B) Representative contour plots of splenic live CD3ε+CD4+ cell subsets (see Supplemental Figure 6D for summary data). (C) Principal component analysis of 1270 differentially expressed genes identified from a generalized linear model and ANOVA-like testing with FDR q < 0.05. Ellipses represent normal contour lines with 1 SD probability. (D) K-means clustering of 1270 genes with an FDR q < 0.05 comparing the cell populations from C scaled as Z-score across rows. (E and F) Fold-change–fold-change plots for iUhrf1+/+ (E) and iUhrf1fl/fl (F) mice of Foxp3-GFP+tdTomato+ versus Foxp3-GFP+tdTomato– and ex-Foxp3 versus Foxp3-GFP+tdTomato– highlighting genes exhibiting an increase (q < 0.05) in Foxp3-GFP+tdTomato+ versus ex-Foxp3 (blue dots) and ex-Foxp3 versus Foxp3-GFP+tdTomato+ (pink dots). Numbers of differentially expressed genes are indicated. (G) Cumulative distribution function plots comparing Foxp3-GFP+tdTomato+ cells from iUhrf1+/+ versus iUhrf1fl/fl mice with each population normalized to the Foxp3-GFP+tdTomato– population sorted from their respective genotypes. The cumulative proportion of all genes (black), a Treg-defining gene set (43) (orange), and the GSE22045_TREG_VS_TCONV_UP gene set (48) (red) are shown. (H) Cumulative distribution function plots as in G comparing the ex-Foxp3 cells from iUhrf1+/+ versus iUhrf1fl/fl mice. n = 5 (iUhrf1+/+); n = 6 (iUhrf1fl/fl). P values resulting from Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests for cumulative distributions comparing all genes against either gene set are shown in G and H.