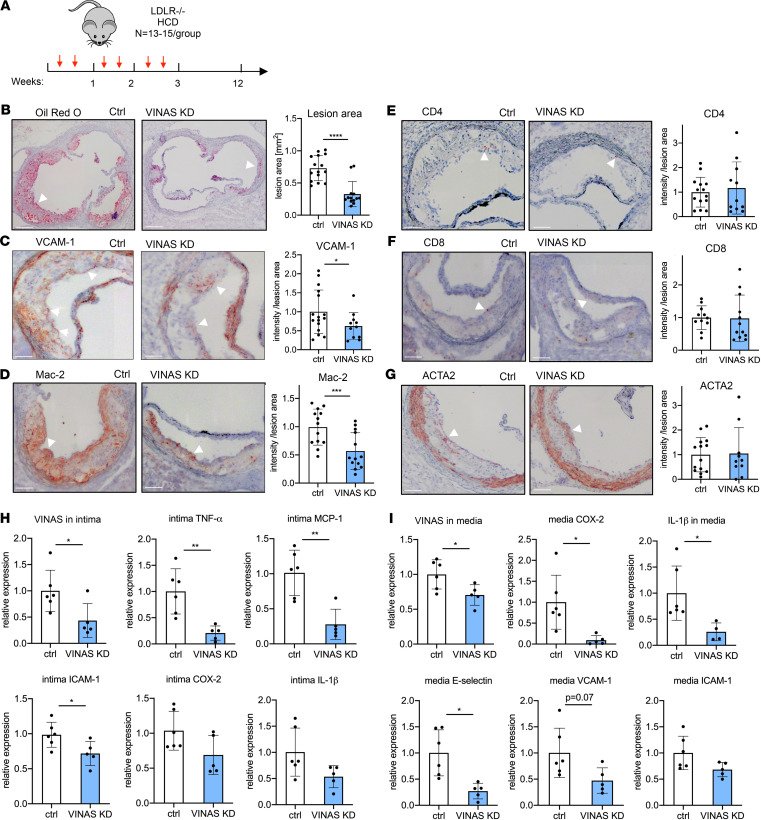
Figure 5. In vivo knockdown of VINAS inhibits atherosclerotic lesion formation by decreasing vascular inflammation.
(A) LDLR–/– mice were i.v. injected with vehicle control gapmeR (n = 15) or VINAS gapmeR (n = 13) twice per week (10 mg/kg/mouse/injection) and placed on an HCD for 12 weeks. Representative images and quantification for Oil Red O (scale bar: 400 μm) (B), VCAM-1 (C), Mac-2 (D), CD4+ (E), CD8+ (F), and ACTA2 (G) staining (arrowhead) of the aortic sinus of LDLR–/– HCD mice treated with control (n = 15) or MAARS (n = 13) gapmeRs for 12 weeks. Scale bar: 100 μm. VINAS silencing efficiency and expression of inflammatory markers was assessed by RT-qPCR in the intima (H) and media (I) fractions of the aortic arch from control gapmeR (n = 6) and VINAS gapmeR groups (n = 5). Data represent the mean ± SD. Statistical differences were calculated using unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.