Figure 4.
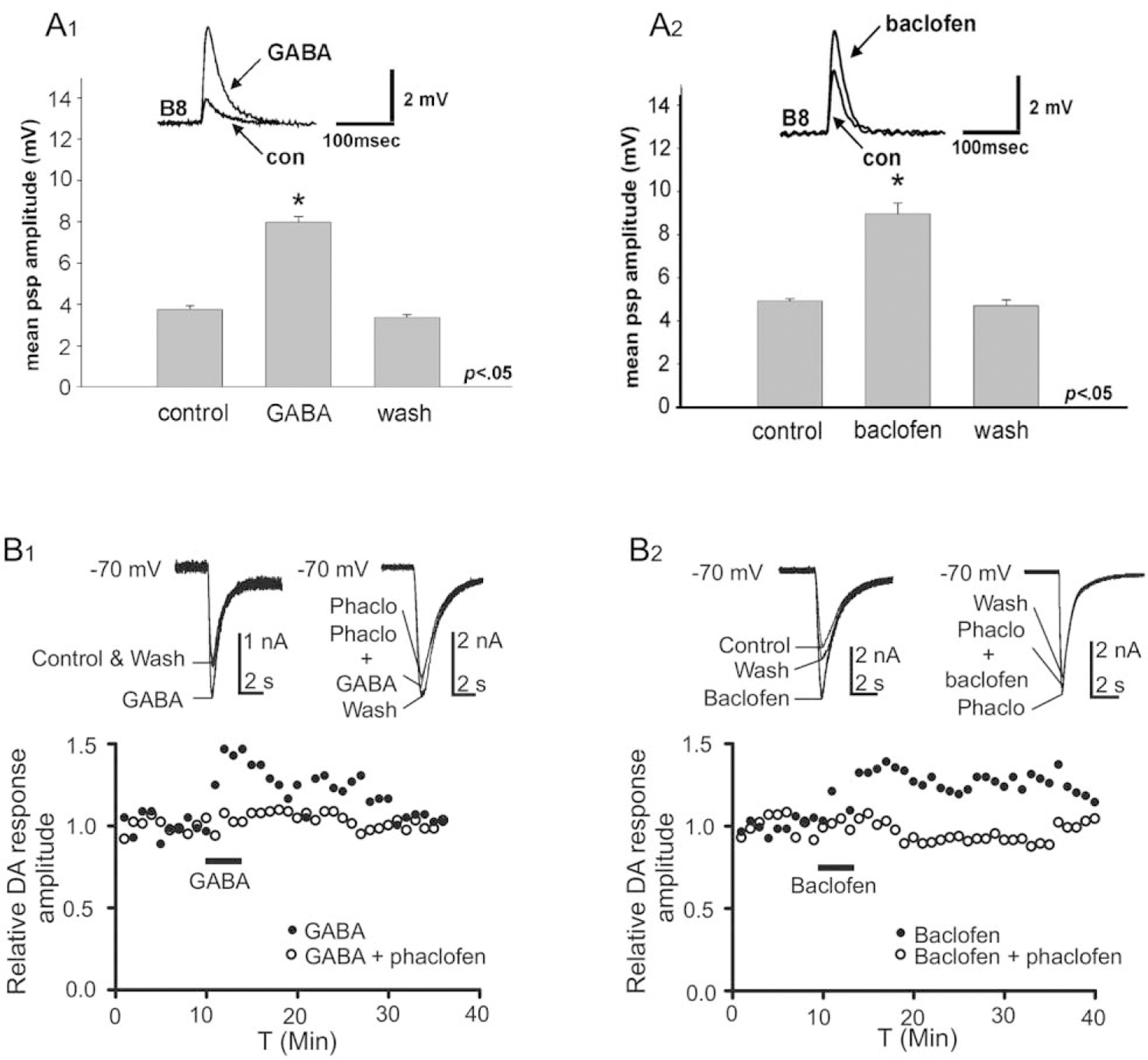
GABA modulates rapid dopaminergic signaling from B20 to the radula closer motor neuron B8. (A1) Bath application of GABA (1 mmol L−1) increased the amplitude of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) produced in B8 by impulses evoked in B20 (con, control). (A2) GABAB agonist baclofen (1 mmol L−1) also augmented the B20-to-B8 EPSP. Reprinted from Díaz-Ríos and Miller, 2005. J. Neurophysiol. 93: 2142–2156, with permission from the American Physiological Society. (B1, B2) GABA and baclofen potentiate dopamine (DA) currents in B8. (B1) Perfusion of GABA (100 μmol L−1) augmented the inward current evoked by dopamine puffed from a micropipette onto the soma of B8. This potentiation was blocked by the GABAB antagonist phaclofen (Phaclo, 100 mmol L−1). (B2) Perfusion of baclofen (100 μmol L−1) also potentiated the inward current evoked by dopamine in B8. The effect of baclofen was also blocked by phaclofen. All experiments were conducted in the presence of tetrodotoxin (10 μmol L−1) to suppress impulses and synaptic activity. Reprinted from Svensson et al., 2014. J. Neurophysiol. 112: 22–29, with permission from the American Physiological Society.
