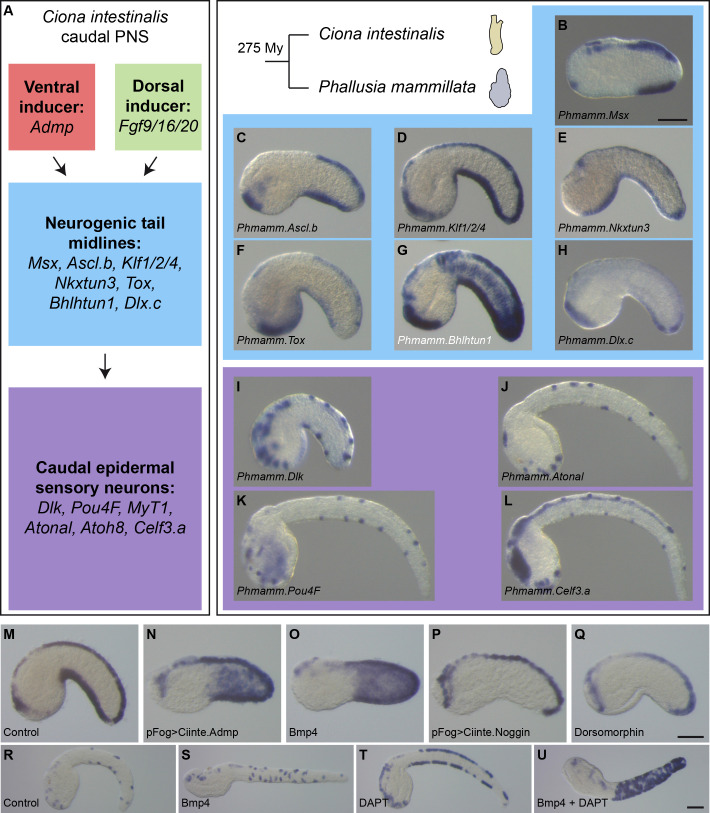
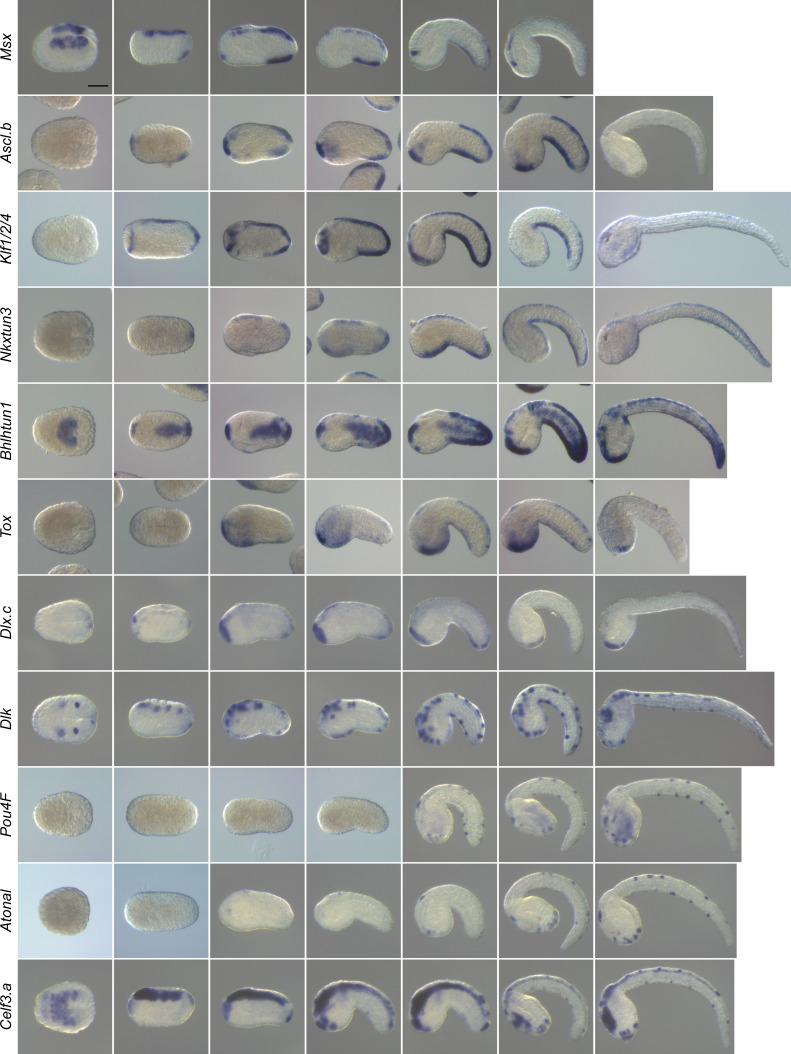
Figure 4. Expression and regulation of caudal PNS genes in Phallusia mammillata.
(A) Schematic summary of caudal PNS specification and molecular regulators in Ciona intestinalis (adapted from Roure et al., 2014; Pasini et al., 2006; Roure and Darras, 2016; Waki et al., 2015; Joyce Tang et al., 2013, more details can be found in Figure 1—figure supplement 1A). (B–L) Expression of the P. mammillata orthologs of the C. intestinalis caudal PNS genes. In situ hybridization of a late neurula for Msx (B), at early tailbud stages for Ascl.b (C), Klf1/2/4 (D), Nkxtun3 (E), Tox (F), Bhlhtun1 (G), Dlx.c (H) and Dlk (I); and at mid/late tailbud stages for Atonal (J), Pou4F (K), and Celf3.a (L). (M–Q) Expression of Phmamm-Klf1/2/4 at early tailbud stages in control embryos (M), following electroporation of pFog >Ciinte.Admp (N) or pFog >Ciinte.Noggin (P); or following treatment with Bmp4 protein (O) or Dorsomorphin (Q). (R–U) Expression of Phmamm.Pou4F at late mid/late tailbud stages in control embryos (R), following treatment with Bmp4 protein (S), DAPT (T) or a combination of Bmp4 and DAPT (U). Embryos are shown in lateral view with dorsal to the top and anterior to the left. Scale bars: 50 μm.