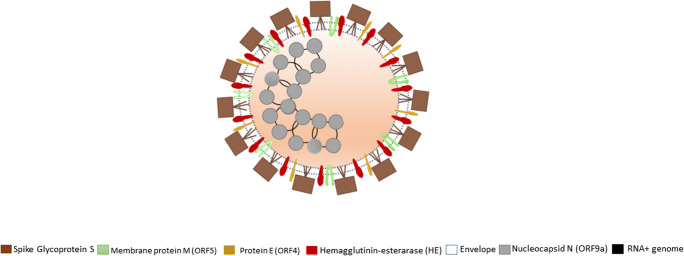
Fig. 2.
Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 structure: glycoprotein S (spike) is cleaved into two glycosylated subunits, S1 (binds to the host’s receptor, ACE2) and S2 (aid viral and host membrane fusion). Membrane protein M aids to the assembly and budding of viral particles to ER-Golgi-intermediate compartment and interacts with ORF9a for RNA packaging into virion. Protein membrane E type III (single pass and forms a homopentameric ion channel, and is a viroporin) interacts with ORF5 and ORF9a, which aids in viral assembly, budding, and pathogenesis. Dimer hemagglutinin-esterase (HE) plays an important role during the release phase of the virus into the host cell. Genome consists of a single strand of large size positive sense RNA (26 to 32 kb in different viruses). Nucleocapsid N (ORF9a) plays its role in genome protection, viral RNA replication, virion assembly, and immune evasion (including IFN-I suppression). It binds to viral genomic RNA, forming a helical ribonucleocapsid and interacts with M and NSP3 proteins. Envelope is the coating of the virus, consisting of a membrane that the virus “inherits” from the host cell after infecting it