Figure 1. Accumulation of B7-H4 is associated with immune-cold breast cancer and reduced PD-L1 expression.
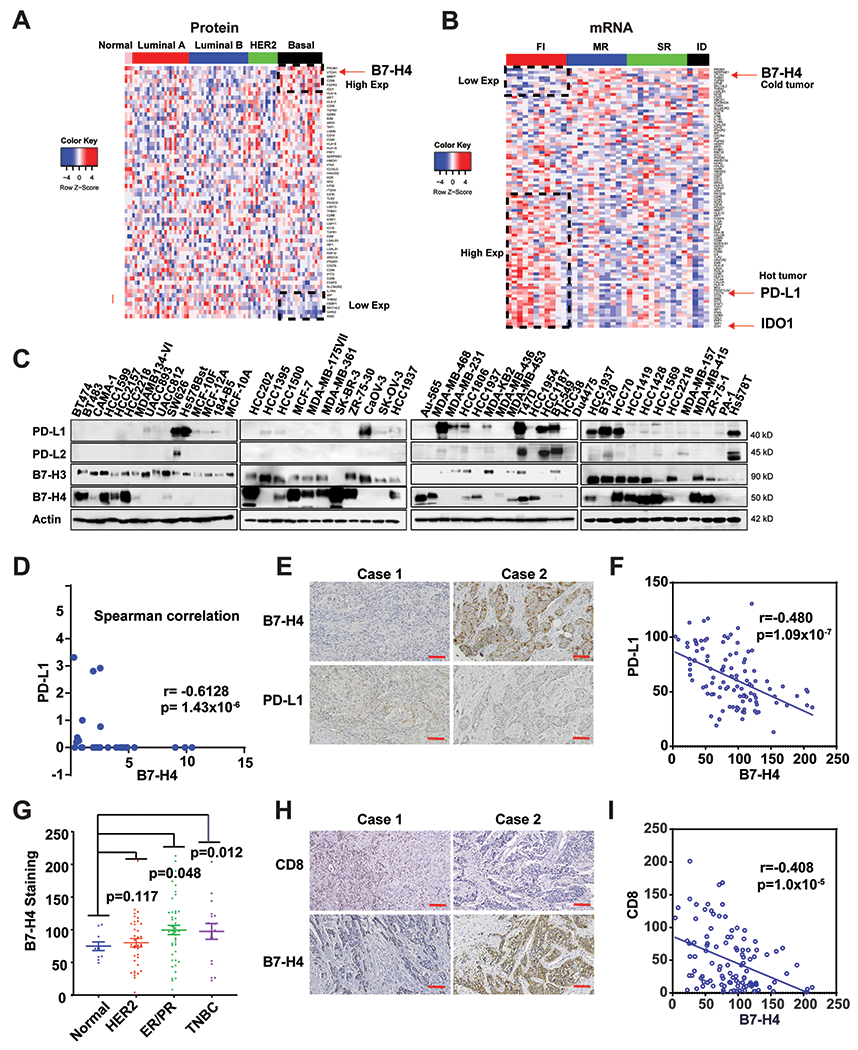
(A) Proteomic analysis of 59 immune-relevant proteins in TCGA samples of PAM50-defined intrinsic subtypes including 25 basal-like, 29 luminal A, 33 luminal B, and 18 HER2-enriched tumors, along with three normal breast tissue samples. The genes (rows) are sorted according to the difference between the average proteomic level in basal subtype and the average proteomic in the other cancer types. (B) Heatmaps depicting expression of immune-relevant genes (mRNA) in the bulk tumor in FI (fully inflamed), SR (stroma restricted), MR (margin restricted) and ID (immune desert) TNBC (n=37). (C) The protein expression of PD-L1, PD-L2, B7-H3 and B7-H4 in 45 breast and 4 ovarian cancer cell lines were measured by immunoblot. (D) Expression of PD-L1 and B7-H4 in the indicated cell lines was quantified using ImageLab. Spearman correlation indicates B7-H4 expression is negatively correlated with PD-L1 expression in the test cancer lines (r = −0.6128, p =1.43x10−6). (E-I) Tissue array of 110 breast invasive ductal carcinoma (including 46 cases of ER/PR positive, 37 cases of Her2 positive and 17 cases of TNBC and 10 adjacent normal tissue specimens) were subjected to immunohistochemistry. (E) Representative paired immunohistochemical staining of B7-H4 and PD-L1. (F) Statistical analysis of immunohistochemical staining indicates B7-H4 expression is negatively correlated with PD-L1 expression in breast cancer tissues (r = −0.480, p =1.09x10−7). (G) The B7-H4 staining in the tissue array was quantified based on the subtypes including ER+/PR+, HER2+, TNBC and normal breast tissue samples. (H) Representative paired immunohistochemistry of B7-H4 and CD8. (I) Statistical analysis of immunohistochemically staining indicates that CD8 T cell number is negatively correlated with B7-H4 expression in breast cancer tissues (r = −0.408, p =1.00x10−5).
