Figure 6. B7-H4 and its ubiquitination or glycosylation-deficient mutants profoundly alter tumor growth and doxorubincin-induced immunogenic cell death.
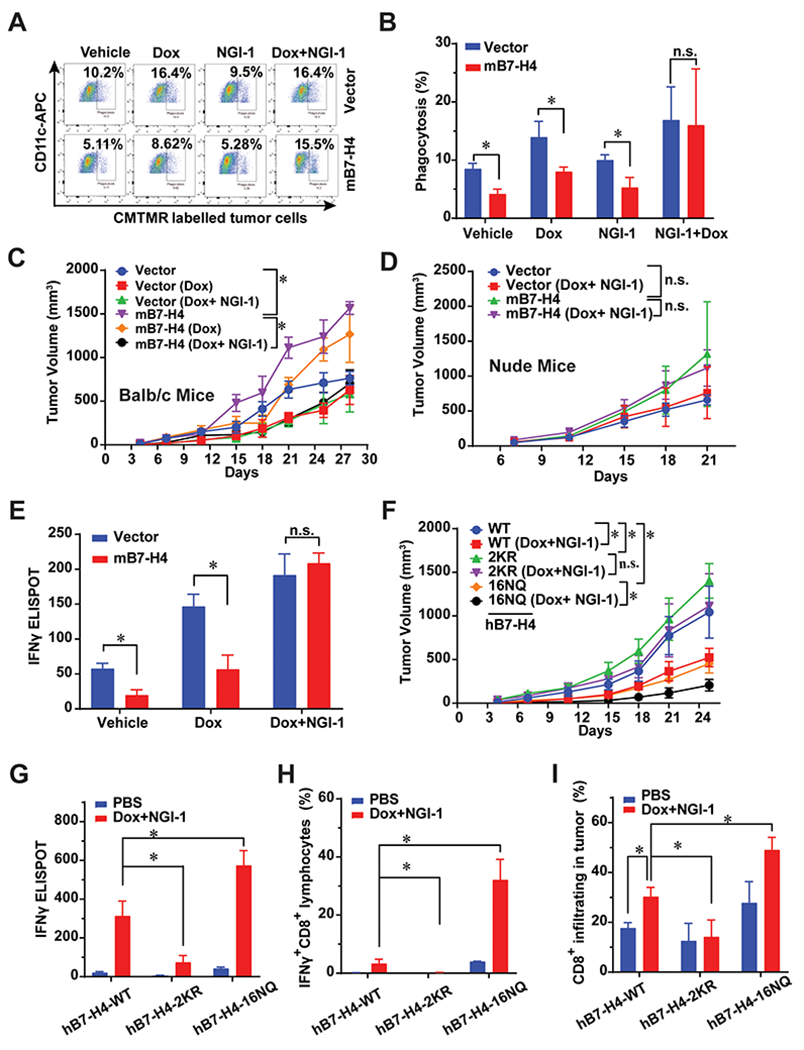
(A-B) In vitro phagocytosis of co-culture of mouse DCs and tumor cells. 4T1-vector and 4T1-B7-H4 cells were treated with doxorubicin (25 μM) or NGI-1 (10 μM) for 24 hour and co-cultured with the purified CD11c positive cells for 2 hours at a ratio of 1: 1, and then subjected to flow cytometry. n=3 mice per group. (C) In vivo vaccination assay. 4T1-vector or 4T1-B7-H4 cells were treated with doxorubincin (Dox, 25 μM) alone or in combination with NGI-1 (10 μM) for 24 h. Then these cells (106 per mice) were orthotopically injected into the right fourth mammary gland of the BALB/c mice (the vaccination step). PBS was used in the non-vaccinated group. One week later, all mice were rechallenged with live 4T1-vector or 4T1-B7-H4 cells (3 × 105 per mouse) of the same kind as the vaccination step in the left fourth mammary gland (the challenge step). The tumor growth was monitored twice per week. n=8 mice per group. (D) Failure of nu/nu BALB/c to mount an immune response against Dox/NGI-1 treated 4T1-vector or 4T1-B7-H4 cells. Nude mice were inoculated with Dox/NGI-1 treated 4T1-V or B7-H4 cells 1-2 weeks before the injection of live 4T1-vector or B7-H4 cells into the opposite flank, the tumor growth was monitored. n=6 mice per group. (E) 4T1-vector or 4T1-B7-H4 cells were treated with doxorubincin (Dox, 25 μM) alone or in combination with NGI-1 (10 μM) for 24 h. These cells were then orthotopically injected into the right fourth mammary gland of the BALB/c mice (the vaccination step). PBS was used in non-vaccinated control group. One or two week later, all mice were challenged with injection of live 4T1-vector or 4T1-B7-H4 cells (the same kind cells as used in the vaccination step) in the left fourth mammary gland (the challenge step). On day 28, mouse spleens of BALB/C mice were harvested and followed by ELISPOT. Quantification of IFNγ ELISPOT is shown. n=3 mice per group. (F-I) In vivo vaccination assays were performed with 4T1-hB7-H4, 4T1-hB7-H4-2KR, and 4T1-hB7-H4-16NQ cells. BALB/c mice were inoculated with Dox/NGI-1-treated 4T1-hB7-H4, 4T1-hB7-H4-2KR, and 4T1-hB7-H4-16NQ cells 1-2 weeks (the vaccination step, PBS was used in the non-vaccinated group) before the injection of the live cells of the same kind (4T1-hB7-H4, 4T1-hB7-H4-2KR and 4T1-hB7-H4-16NQ cells) into the opposite mammary gland (the challenge step), (F) the tumor growth was monitored. n=10 mice per group. (G) On day 28, mouse spleens were harvested and followed by IFNγ ELISPOT. Quantification of IFNγ ELISPOT is shown. n=3 mice per group. PBS is used in non-vaccinated group. (H) On day 28, mouse spleens were harvested and followed by flow cytometry of staining IFNγ and CD8. Quantification of IFNγ+CD8+cells is shown. n=3 mice per group. PBS is used in non-vaccinated control group. (I) On day 28, mouse tumors in the mammary gland were harvested and digested followed by flow cytometry by detecting CD45 and CD8. n=3 mice per group. PBS is used in non-vaccinated control group. Quantification of CD8+ infiltrating cells is shown.
