Figure 3.
Model Prediction and Experimental Confirmation of GEF-H1 Concentration-Dependent Switching of Rho Activity Dynamics by Optogenetic Tuning
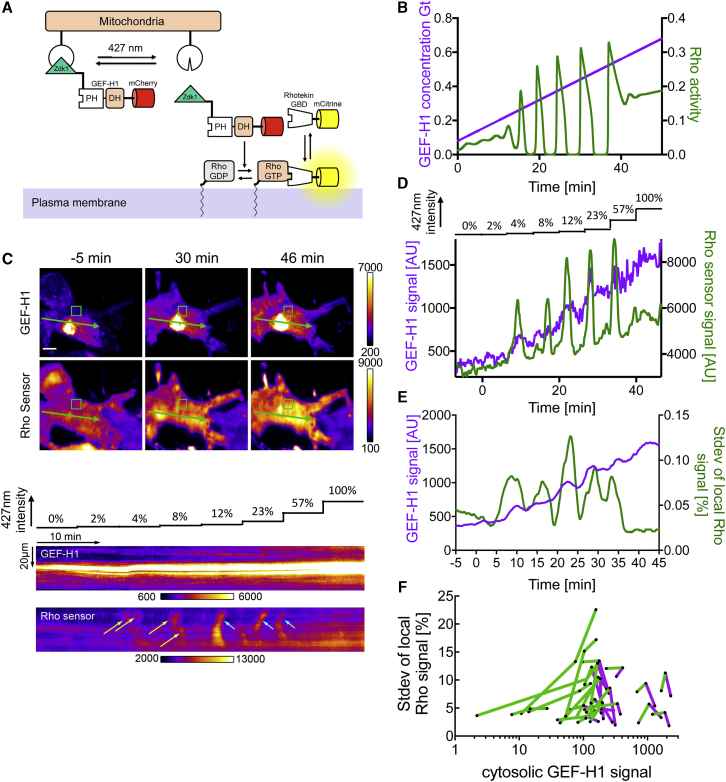
(A) A schematic representation of GEF-H1 release from mitochondria to tune the effective cytosolic GEF-H1 concentration with light.
(B) Simulation of Rho activity dynamics with linearly increasing total concentration of GEF-H1 (GT).
(C–F) The dependence of Rho sensor activity dynamics on the effective, cytosolic GEF-H1 concentration was analyzed in U2OS cells expressing the LOV domain targeted to mitochondria (TOM20-LOV2), mCherry-Zdk1-GEF-H1(C53R), and a Rho sensor (mCitrine-Rhotekin-GBD).
(C–E) Analysis of a representative cell.
(C) Top: TIRF images of mCherry-Zdk1-GEF-H1(C53R) and the Rho sensor (see also Video S4). Bottom: kymographs corresponding to green arrows in top panel. Yellow arrows point to Rho activity pulses, cyan arrows point to Rho activity waves.
(D) Cytosolic mCherry-Zdk1-GEF-H1(C53R) levels obtained as the minimum signal in green boxed regions in (C), and measurements of the Rho activity sensor signal over the time course of the experiment.
(E) The local standard deviation of Rho activity signals over the time course of the experiment, using a shifting time-interval of 15 frames, average of all central cell regions of the cell shown in (C), and cytosolic mCherry-Zdk1-GEF-H1(C53R) levels (moving average of 15 frames corresponding to 2.5 min).
(F) Plot of local standard deviation of Rho activity signals against cytosolic mCherry-Zdk1-GEF-H1(C53R) levels from all of the analyzed cells (n = 23 cells from 3 experiments). Lines connect 3 data points that represent the following time intervals of optogenetic tuning experiments: the average of the initial 10 frames, the intermediate frames, and the last 10 frames. Lines with net increase of local Rho activity standard deviation are in green, lines with net decrease are in magenta.
(E and F) Percentage (%) indicates percentage of mean intensity.
Scale bars: 10 μm.
See also Figure S4.