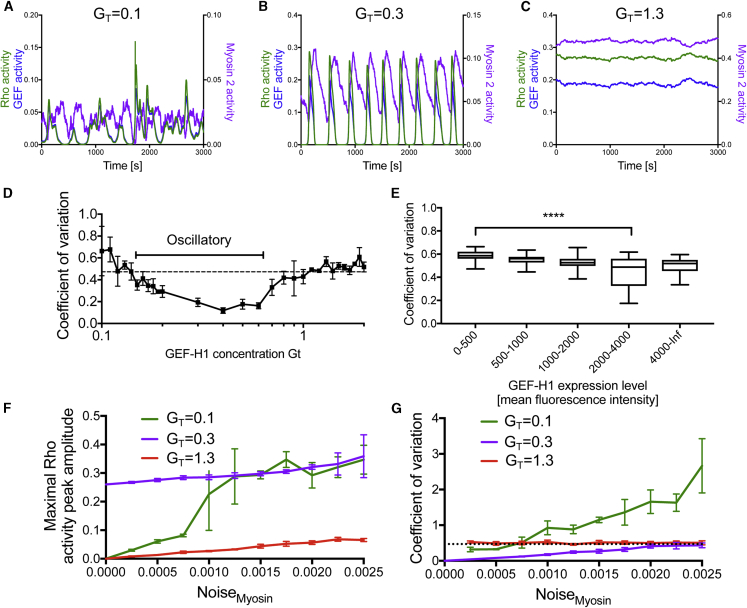
Figure 4.
Sensitivity of Rho Activity Pulses to Stochastic Myosin Inputs
Numerical simulations of the system of stochastic differential equations (Equations 4, 5, and 6) that include extrinsic additive noise in the myosin component to represent extracellular and intracellular inputs.
(A–C) SDE simulations at low (A), intermediate (B), and high (C) cytosolic concentrations of GEF-H1 (GT).
(D) Measurement of the coefficient of variation (CV) of the Rho activity interpeak distance in SDE simulations at various cytosolic concentrations of GEF-H1 (GT). The black bar indicates the range of GT that generates oscillatory dynamics in the absence of noise.
(E) Measurement of the CV of the Rho activity interpeak distance in experiments at varying expression levels of active, microtubule-binding deficient GEF-H1(C53R) mutant (n = 91 cells from 3 experiments; box and whisker plot; ∗∗∗∗1-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post test, p < 0.0001).
(F) Dependence of maximal Rho activity peak amplitude on extrinsic noise levels in the myosin component (Noisemyosin) at low, intermediate, and high GEF-H1 concentrations (GT).
(G) Dependence of the CV of the Rho activity interpeak distance on extrinsic noise levels in the myosin component at low, intermediate, and high GEF-H1 concentrations (GT).
Dotted black line in (D) and (G): CV of Gaussian input noise. (D), (F), and (G): mean and SD from 3 independent simulations.