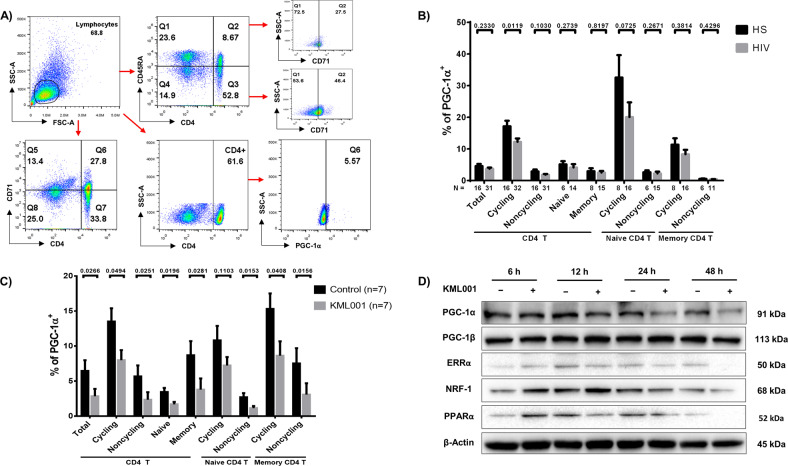
Fig. 3. KML001 disrupts CD4 T cell homeostasis and represses key PGC-1α targets in a time-dependent manner.
A Representative dot plots for flow cytometry gating strategy for lymphocytes, naive and memory, cycling and non-cycling, CD4, and PGC-1α in PBMCS from PLHIV or HS. B, C Flow cytometry analysis of the frequencies (%) of PGC-1α+ cells in total, cycling (CD71+), non-cycling (CD71−), naive (CD45RA+), and memory (CD45RA−), cycling naive (CD71+ CD45RA+), non-cycling naive (CD71− CD45RA+), and cycling memory (CD71+ CD45RA−), and non-cycling memory (CD71− CD45RA-) CD4 T cell subsets in PBMCs isolated from people living with HIV (PLHIV) versus healthy subjects (HS) (B) or in CD4 T cells after treatment with KML001 or DPBS for 48 h (n = 7) (C). D Representative images of western blot analysis of PGC-1α, PGC-1β, ERRα, and NRF-1, and PPARα expressions in CD4 T cells treated with KML001 or DPBS for 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. All summary data are shown as mean ± SEM.