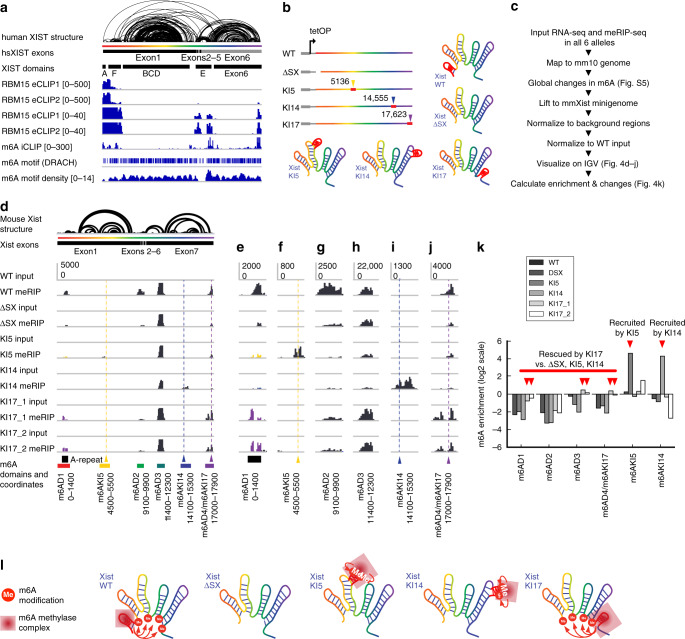
Fig. 4. XIST RNA structure determines m6A modification patterns.
a m6A on the human mature XIST RNA. K562 RBM15 eCLIP was normalized against input in 100-nt windows36 and plotted in two scales to highlight the differences in binding the 5’ end and other regions. HEK293 cell m6A iCLIP track was from ref. 47. m6A motif density was calculated in 300-nt windows and 50-nt steps. b Gene structure for the alleles. WT and ΔSX (~900 bp deletion in Xist 5’ end) alleles were under the control of tetracycline-inducible promoter. A-repeat relocation alleles KI5, KI14, and KI17 were derived from ΔSX by A-repeat insertion in the indicated locations. c MeRIP-seq analysis pipeline. Global analysis of m6A changes was performed on data mapped to the mm10 genome, while targeted analysis was performed on the mature mouse Xist transcript. d m6A sites are changed after relocating the A-repeat domain. The mouse Xist RNA PARIS model is the same as in Fig. 3a. m6A domains are labeled under the genome browser tracks. Y-axis is the same in each track. All data including the A-repeat relocation alleles were mapped to the same wild-type Xist mature RNA. e–j Zoom-in view of all m6A domains. Location of the original A-repeat is indicated in e. The A-repeat knockin locations are indicated in f, i, j. Y-axis scales are the same for all tracks. k Quantification of m6A changes relative to wild type in log scale in pre-defined m6A domains shown in d. One replicate was available for each sequencing library. l A mechanistic model of RNA structures in guiding m6A modifications. The A-repeat domain recruits the m6A methylase complex to modify sequences physically close to the domain. The residual modification on Xist after A-repeat deletion was due to its intrinsic ability to recruit m6A methylase complex. Relocation of the A-repeat to the inside of the large domains (KI5 and KI14) induces local modifications (m6AKI5 and m6AKI14). Relocation of the A-repeat to the end of the transcript (KI17) induces modification in physical proximity (m6AD1, m6AD2, m6AD3, and m6AD4). Source data are provided as a Source data file.