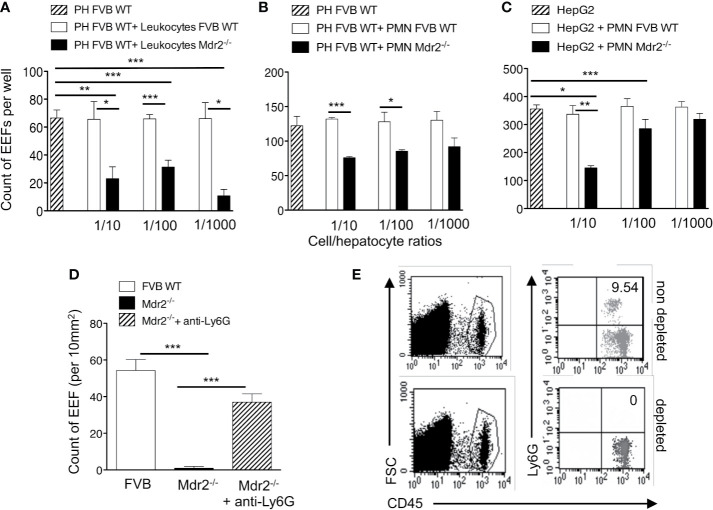
Figure 4.
Impairement by neutrophils of intra-hepatic parasite development in Mdr2-/- mice. Infection of primary hepatocytes (PH) isolated from naïve 6-week-old female WT FVB mice co-cultured with liver resident leukocytes (A) or with neutrophils isolated from the bone marrow of naïve 6-week-old female WT FVB and Mdr2-/- mice (B). In parallel, Infected HepG2 cell line was co-cultured with bone marrow neutrophils isolated from naïve 6-week-old female WT FVB and Mdr2-/- mice. 1/10, 1/100 and 1/1000 reflect the ratios of leucocytes over hepatocytes (A) and neutrophils (PMN) over hepatocytes (B, C). The number of EEFs was determined in five independent wells per condition using fluorescence microscopy (objective × 20) at 40 h p.i. with PbANKA. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Measurement of EEFs by fluorescence microscopy (objective × 10) in the liver of WT FVB, and Mdr2−/− controls and in neutrophil depleted-Mdr2−/− mice 24 h p.i. with 104 PbANKA SPZ (Mann–Whitney test; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). (E) Assessment of neutrophil depletion efficacy: FACS dot plot analysis in the blood of 6-week-old female Mdr2−/− mice treated with the neutrophil depleting antibody anti-Ly6G or with an irrelevant antibody. Neutrophils are stained using CD45 and Ly6G markers. PH, primary hepatocyte; PMN, polymorphonuclear cells.