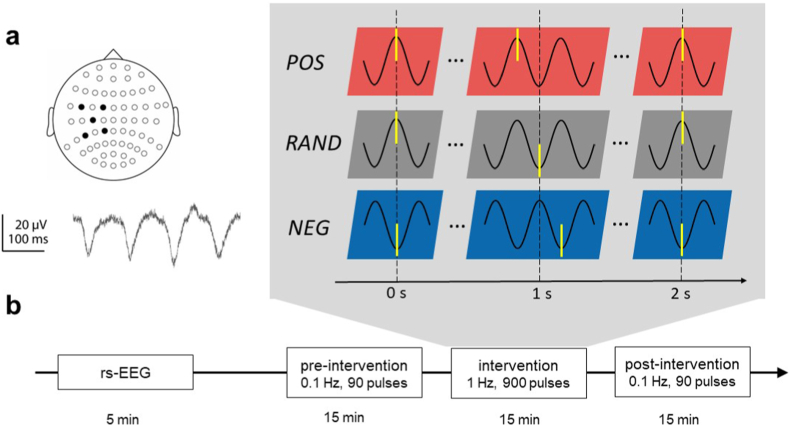
Fig. 1.
Experimental design. a μ-rhythm was derived using a 5-channel (black dots) Laplace transform centered on EEG sensor C3 (top), an example raw data trace is shown at the bottom. b Plasticity sessions started with a 5 min resting-state EEG (rs-EEG) to test the accuracy of our phase triggering algorithm. Thereafter, each plasticity session contained a block of 90 single TMS pulses at a rate of 0.1 Hz before and after the rTMS intervention block, with TMS pulses applied irrespective of the EEG signal (“open loop”). For the intervention block, a double-blind, randomized crossover design was applied, so that each participant received 900 pulses of ∼1 Hz rTMS in the positive peak condition (POS), 1 Hz rTMS in the random phase (RAND, irrespective of μ-rhythm) or ∼1 Hz rTMS in the negative peak condition (NEG). Time points of stimulation are indicated schematically by yellow bars. TMS was applied to the hand representation of left primary motor cortex. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)