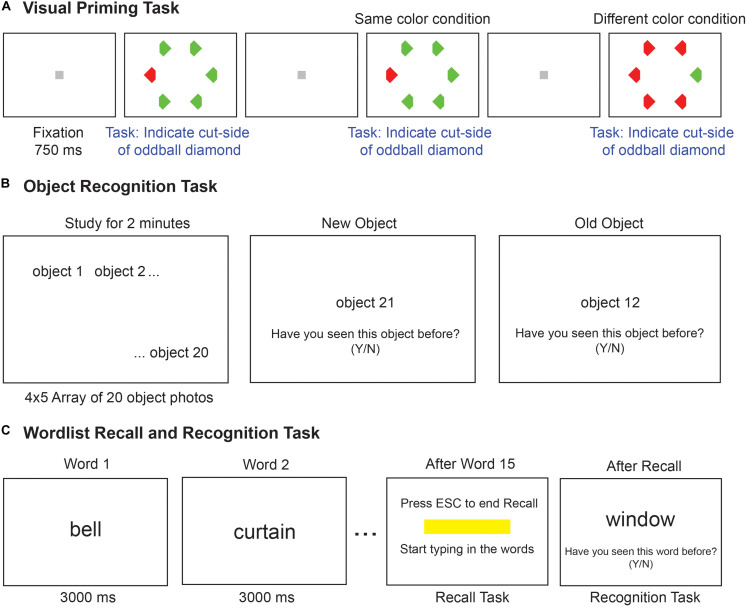
FIGURE 1.
Implicit and explicit memory tasks. (A) Schematic of the visual priming task with its two possible conditions. Each trial started with a gray fixation square followed by a search array. The second trial shows the odd–colored target with the same color (red) as the previous target, hence it is the same-color condition. The next trial shows the case where the target color (green) is different from the previous trial (red), hence it is the different-color condition. Participants make faster responses on same-color trials compared to different-color trials, indicative of an implicit memory. (B) Schematic of the object recognition task. Participants were asked to study a set of 20 common object photographs for 2 minutes. In the test phase (second and third panels), one picture was shown at a time and participants had to indicate whether the object was shown or not shown during the study phase. (C) Schematic of the word recall and recognition tasks. During the study phase (left panel), 15 words are presented for 3 s each in a sequence. In the recall phase (middle panel), a text box appeared on the screen, and the experimenter typed in the words recalled verbally by the participant. In the recognition task (right panel), 30 words were presented in sequence, and participants had to indicate whether the word was shown or not during the study phase.