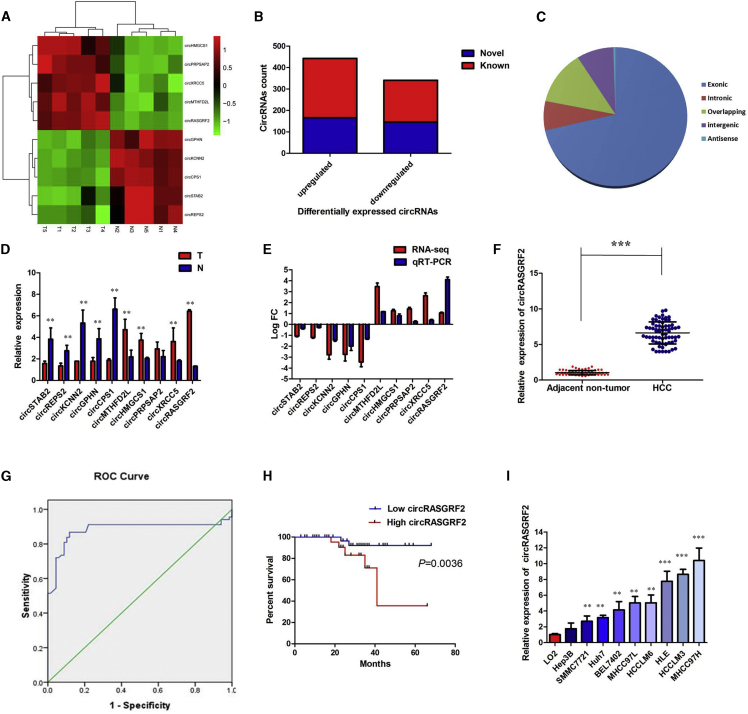
Figure 1.
circRNA profiling in human HCC tissues and circRASGRF2 characterization
(A) Heatmap shows the top 10 dysregulated circRNAs between five pairs of HCC and adjacent noncancerous liver (ANL) tissues. (B) Among the 784 differentially expressed circRNAs, 313 circRNAs were verified as novel circRNAs; 473 circRNAs were identified beforehand and listed in the circRNA database. (C) The 784 identified circRNAs were divided into five different categories on the basis of the way they were produced. (D) Expression levels of top 10 dysregulated circRNAs were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. (E) Comparison of log2 fold changes (FCs) in circRNAs between circRNA RNA-seq and quantitative real-time PCR results. (F) The level of circRASGRF2 was significantly increased in HCC tissues compared to ANL tissues. (G) Evaluation of the diagnostic performance of circRASGRF2 for HCC diagnosis. (H) Kaplan-Meier curve revealed that high expression of circRASGRF2 was relative to a poor overall survival in HCC patients. (I) The levels of circRASGRF2 were significantly increased in HCC cell lines compared to the normal liver cell line L02. All tests were performed at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.