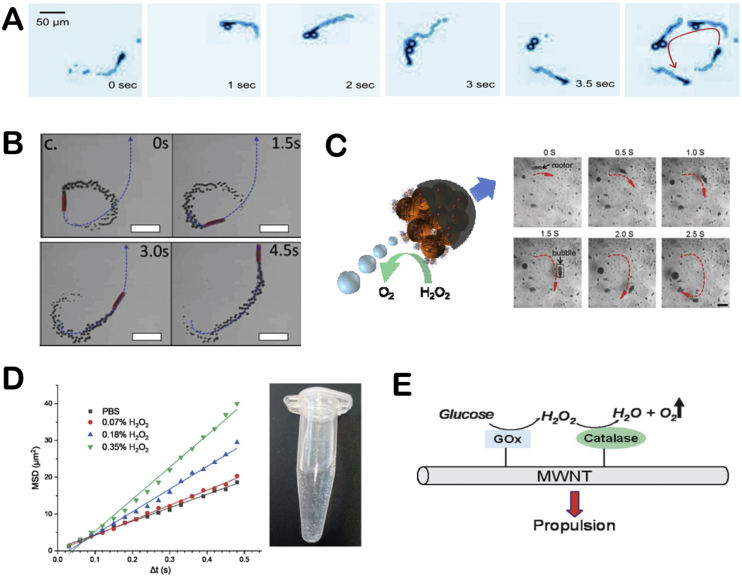
Fig. 8.
The bubble propulsion mechanisms of EMNMs. (A) The motion of the hybrid microengine was powered by the generation of “front-side bubbles”. Reproduced with permission from ref 28. Copyright 2010, American Chemical Society. (B) The trajectory of the catalase-modified microrocket in 0.1 wt% H2O2 solution. Reproduced with permission from ref 94. Copyright 2016, Wiley. (C) The schematic illustration of propulsion of the bio-catalytic Janus motor and a video clip of the motor's trajectory. Reproduced with permission from ref 97. Copyright 2014, Royal Society of Chemistry. (D) The change of MSD values and the formation of oxygen bubbles with the addition of H2O2. Reproduced with permission from ref 14. Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry. (E) The propulsion mechanism of MWCNTs decorated with GOx and catalase. Reproduced with permission from ref 55. Copyright 2008, Royal Society of Chemistry.