Table 1.
The classification and introduction of EMNMs.
| Types of EMNMs | Movement mechanism | Materials | Fuel | Motion environment | Motion speed | Application | Schematic diagram | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule motors and enzymes as motors | Synthesis and decomposition of ATP | Myosin, dynein and kinesin | ATP | – | – | – |  |
16,17,18 | ||
| Synthesis and decomposition of ATP | ATP synthase | ATP | – | – | – | 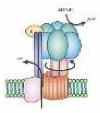 |
20 | |||
| Enzyme-enhanced diffusion | Urease | Urea | Water | – | – |  |
24 | |||
| Enzyme-enhanced diffusion | DNA polymerase | Nucleotide | Buffer solution | – | Micro/nanopump |  |
26 | |||
| Single enzymatic reaction propelled EMNMs | Catalase | Bubbles propulsion | Ti/Au film | H2O2 | Water | 226.1 ± 21.1 μm/s in 1.5% H2O2 | – |  |
28 | |
| Bubbles propulsion | Fpoly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate and dextran | H2O2 | Water | 102.96 ± 2.08 μm/s in 4% H2O2 | – |  |
32 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Mesoporous silica | H2O2 | Water | – | Drug delivery |  |
34 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Organoclay/DNA semipermeable microcapsules | H2O2 | Water | – | Motor functionalization |  |
36 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Biotinylated polymer vesicles | H2O2 | Water | – | Biomedical application | 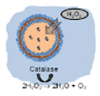 |
39 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Bovine serum albumin/poly- l-lysine (PLL/BSA) multilayer | H2O2 | PBS solution | 68 μm/s in 0.5% H2O2 |
Drug delivery |  |
112 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Polymer capsules | H2O2 | – | 232 μm/s in 2% H2O2 | Drug delivery |  |
96 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Janus Au–mesoporous silica | H2O2 | PBS solution | – | Drug delivery |  |
113 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Metal–organic frameworks | H2O2 | – | – | Drug delivery |  |
37 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Polymersomes | H2O2 | – | – | Drug delivery |  |
33 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Polymer based bottlebrush | H2O2 | a viscous tumor microenvironment gel model |
– | Overcoming tissue penetration barrier |  |
35 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | PEDOT/Au bilayer microtubes | H2O2 | Water | 54.0 ± 3.5 μm/s in 2% H2O2 |
Biochemical sensing |  |
29 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | PEDOT/Au bilayer microtubes | H2O2 | Water | 380 μm/s in 2% H2O2 |
Biochemical sensing |  |
120 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | PEDOT/Au microtubes | H2O2 | Water | 411 ± 40 μm/s in 5% H2O2 |
Biochemical sensing |  |
124 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | PEDOT-PSS/Au microtubes | H2O2 | Water | ~51 μm/s in 0.25% H2O2 |
Biochemical sensing |  |
30 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Multi-metallic (Au/Ag/Ni/Au) | H2O2 | Water | ~209 μm/s in 1.5% H2O2 | Biochemical sensing |  |
95 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Iron oxide particles | H2O2 | Water | – | Biochemical sensing |  |
125 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | PSMA/PS mixtures | H2O2 | PBS solution | 19–69 μm/s in 3.5% H2O2 | Biochemical sensing |  |
127 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Silk fibroin | H2O2 | – | – | Microstirrers |  |
131 | |||
| Bubbles propulsion | Plant tissues | H2O2 | Water | – | Environmental remediation |  |
41 | |||
| Urease | Phoretic propulsion | Silica | Urea | Water | ~5.25 μm/s in 0.1 mol/L urea | Biomedical application |  |
42 | ||
| Phoretic propulsion | Mesoporous silica | Urea | Water | ~8 μm/s in 0.05 mol/L urea | Drug delivery |  |
15 | |||
| Phoretic propulsion | Protein | Urea | PB solution | 2.7 ± 0.2 μm/s in 0.1 mol/L urea | Biomedical application | 45 | ||||
| Phoretic propulsion | Mesoporous silica | Urea | Water and ionic media | – | Drug delivery |  |
43 | |||
| Phoretic propulsion | Mesoporous silica | Urea | Water and PBS | – | Drug delivery |  |
44 | |||
| Phoretic propulsion | Mesoporous silica | Urea | Urine | – | Targeted bladder cancer therapy |  |
117 | |||
| Phoretic propulsion | Platelet cell | Urea | PBS solution | – | Drug delivery |  |
118 | |||
| Phoretic propulsion | Mesoporous silica | Urea | Ficoll solutions | – | Drug delivery |  |
119 | |||
| Phoretic propulsion | Mesoporous SiO2 | Urea | Water | 6.49 μm/s in 0.05 mol/L urea solution | Photodynamic therapy |  |
90 | |||
| Phoretic propulsion | Mesoporous silica | Urea | PBS solution | – | Biochemical sensing |  |
126 | |||
| Other enzymes | ATPase | Phoretic propulsion | Phospholipid vesicles | ATP | Buffer solution | – | – | 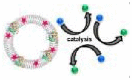 |
48 | |
| Nicking enzyme | Nicking enzyme that cuts tracks | DNA and restriction enzyme | – | – | 0.1 nm/s | – | 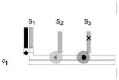 |
51 | ||
| RNase H | Hydrolysis of hybridized RNA | DNA and RNA | RNase H | – | – | – |  |
52 | ||
| Lipase | – | Mesoporous silica | triacetin | PBS solution | – | Environmental remediation | 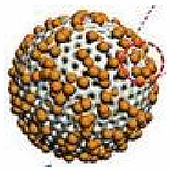 |
50 | ||
| GOx-Cat | Bubbles propulsion | Asymmetric polymersome | Glucose | – | – | Drug delivery | 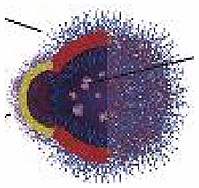 |
116 | ||
| Catalase, urease, lipase, GOx | – | – | H2O2, Urea, Glucose |
– | – | Micropumps |  |
128 | ||
| Multiple enzymes | GOx bilirubin oxidase | Electrophoresis | Carbon fiber | Glucose | Buffer solution | ~1 cm/s in 0.01 mol/L glucose | – | 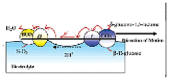 |
53 | |
| GOx and catalase | Bubbles propulsion | Carbon nanotubes | Glucose | Water | – | – | 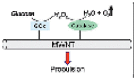 |
55 | ||
| GOx and catalase | Bubbles propulsion | Colloids | Glucose | Buffer solution | – | Drug delivery | 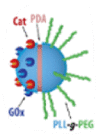 |
56 | ||
| GOx and catalase | Bubbles propulsion | Polymer | Glucose | – | ~11 μm/s in 0.01 mol/L glucose | Drug delivery |  |
57 | ||
| GOx and catalase | Bubbles propulsion | Polymer | Glucose | – | – | – |  |
58 | ||
| GOx and catalase | Bubbles propulsion | Metal–organic frameworks | Glucose | – | – | Photodynamic therapy |  |
59 | ||
| GOx and catalase | Bubbles propulsion | Carbonization of L-CNF | Glucose | Water | ~0.4 μm/s in 0.01 mol/L glucose | – |  |
60 | ||
| GOx and trypsin | Bubbles propulsion and phoretic propulsion | Inorganic substance | Glucose, BA-Rho-110 | Water | 0.72 μm/s in 0.4 mol/L glucose and 0.1 μmol/L BA-Rho-110 solution | – |  |
61 | ||
