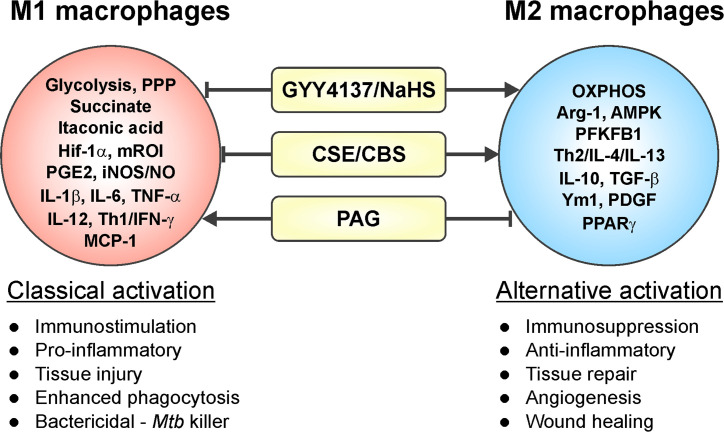
Figure 4.
Involvement of H2S in macrophage polarization. Increased levels of H2S in an inflammatory macrophage model (caused by stimuli such as IFN-γ, LPS, or Mtb infection) trigger a phenotypic shift in macrophages leading to an increased M2 phenotype. On the other hand, reduced H2S levels induce a pro-inflammatory response, which drives macrophages toward an M1 phenotype. Hence, H2S can trigger M1 to M2 macrophage polarization with few exceptions.