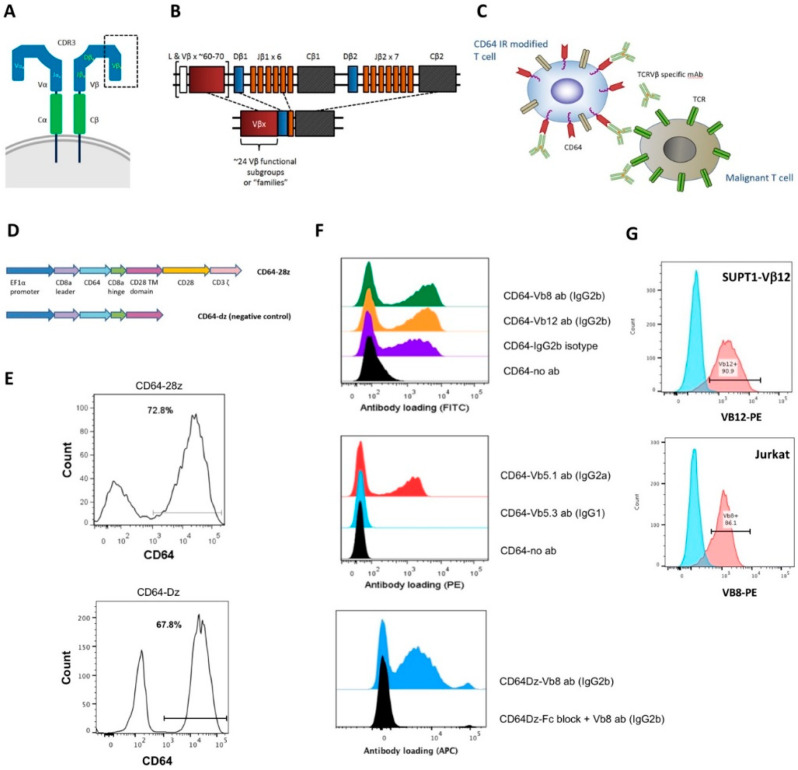
Figure 1.
CD64 IR-modified T cells can be directed toward target T cells via TCRVβ specific antibodies. (A) Schematic structure of α/β T cell receptor (TCR). (B) V(D)J recombination at the TCR β locus. (C) Schematic representation of CD64 IR-transduced T cells being directed toward a target malignant T cell via TCRVβ-family-specific mAb. (D) Schematic structure of CD64-IR construct. (E) Transduction efficiency of primary activated T cells as indicated by staining with CD64 antibody. (F) T cells transduced to express CD64-IR were stained with TCR Vβ-directed antibodies of different isotypes and analyzed by flow cytometry. CD64-IR can be loaded with mouse IgG2a and IgG2b mAb, but not IgG1. CD64 dz T cells share same CD64 extracellular domain as CD64 IR and likewise can be loaded with IgG2b mAb. Fc block prevents antibody loading onto CD64 extracellular domain. (G) Target cells lines were characterized by staining with TCR Vβ-directed antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. The engineered target Sup T1 cell line expresses Vβ12 TCR. Parental SupT1 cells are shown as negative control. Jurkat cells express Vβ8 compared to an isotype control.