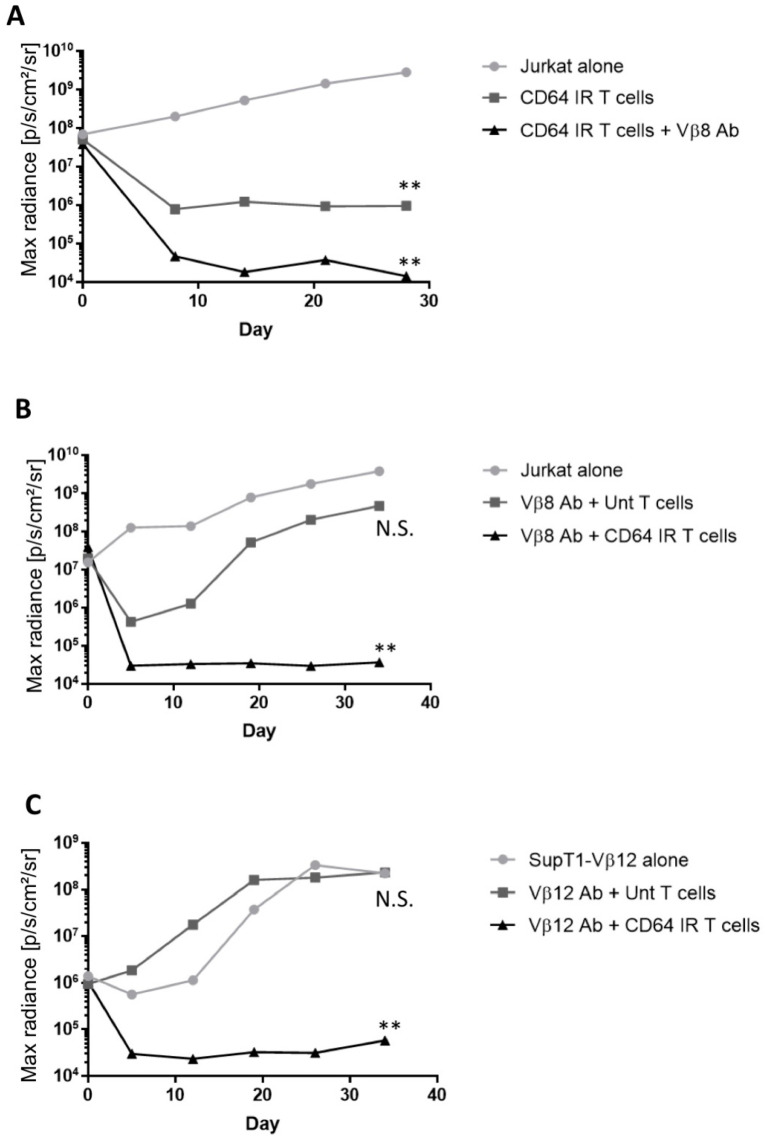
Figure 3.
Vβ antibody in conjunction with CD64 IR T cells prevents T cell malignancy outgrowth in vivo. Winn assays are performed by subcutaneous injection of malignant T cell line, Vβ antibody, and T cells as indicated in immunodeficient mice. Median radiance is graphed and significance level indicated by asterisks are in reference to the malignant T cell line only control. (A) A pilot Winn assay of CD64 IR T cells and Vβ8 antibody with the Jurkat T cell line. Two mice per group. (B) Winn assay of CD64 IR or untransduced T cells and Vβ8 antibody with Jurkat T cell line. Five mice per group. (C) Winn assay of CD64 IR or untransduced T cells and Vβ12 antibody with the engineered SupT1-Vβ12 T cell line. Five mice per group. Against the Jurkat cell line, co-administration of CD64 IR T cells slowed the growth of the Jurkat cells compared to mice given tumor only. Addition of Vβ8 antibody was seen to further inhibit tumor growth in this experiment. In all experiments, groups given Vβ antibody in conjunction with CD64 IR T cells resulted in statistically significant decreased tumor growth. Administration of untransduced cells in conjunction with Vβ antibody did not significantly affect tumor growth. Asterisk coding in figures is as follows: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001.