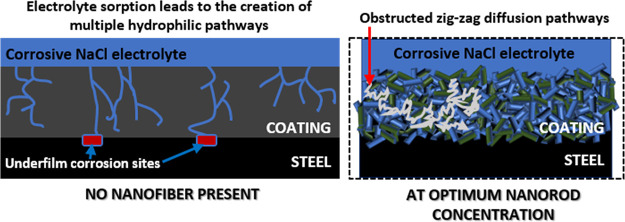
Figure 6.
Mechanism of corrosion protection by niobia nanofibers. LHS: Without the nanofibers, the migration patterns toward the metal surface start with electrolyte sorption. Inherent microcracks within the coating network then allow for unhindered hydrophilic transport channels of corrosive molecules toward the metal surface, leading to the creation of wider cathodic corrosion sites.41,46 RHS: The nanofibers further reinforced the internal microstructures of the niobium oxide/acrylate nanocomposite coating by creating mechanically interlocked, compact, and cross-linked coating networks. This subsequently retarded diffusion routes by blocking the permeating streams of corrosive electrolytes. Since the anticorrosive nanofibers also facilitate pore impermeability, diffusion pathways are zig-zag (i.e., in long meandering lines that curl and loop in irregular patterns), taking a significantly long time for the corrosive electrolyte to reach the metal surface; hence, corrosion is inhibited.46,47