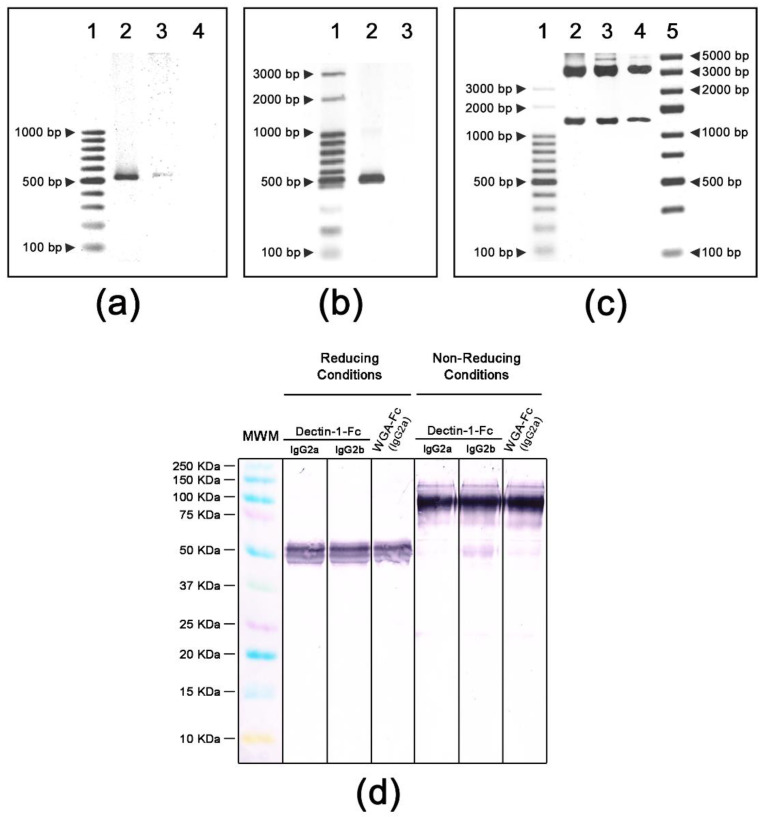
Figure 1.
Construction of lectin-Fc(IgG) fusion proteins and expression as dimers of lectin-Fc(IgG) monomers linked by disulfide bonds. (a) PCR amplification of pFUSE-Dectin-1-Fc. Lane 1—molecular weight marker GeneRulerTM 100 pb DNA (Thermo Fisher Scientific); lane 2—p pFUSE-Dectin-1(IgG2a); lane 3—pFUSE-Dectin-1-Fc(IgG2b) and lane 4—negative control. (b) PCR amplification of pFUSE-WGA-Fc(IgG2a). Lane 1—molecular weight marker Ladder 100 pb (Ludwig Biotec); lane 2—pFUSE-WGA-Fc(IgG2a) and lane 3—negative control. (c) Endonuclease digestion of pFUSE-lectin-Fc(IgG) plasmids: lane 1—molecular weight marker GeneRulerTM 100 pb DNA (Thermo Fisher Scientific); lane 2—pFUSE-Dectin-1-Fc(IgG2a); lane 3—pFUSE-Dectin-1-Fc(IgG2b); lane 4—pFUSE-WGA-Fc(IgG2a) and lane 5—GeneRulerTM Express DNA (Thermo Fisher Scientific). (d) Immunoblots of lectin-Fc(IgG) fusion proteins Dectin-1-Fc(IgG2a), Dectin-1-Fc(IgG2b) and wheat germ agglutinin(WGA)-Fc(IgG2a) showing the monomers of the lectin-Fc(IgG) fusion proteins of ~50 KDa under reducing conditions in comparison to the dimers of lectin-Fc(IgG) of ~100 KDa observed under non-reducing conditions. The molecular marker—Kaleidoscope™ (Bio-Rad).