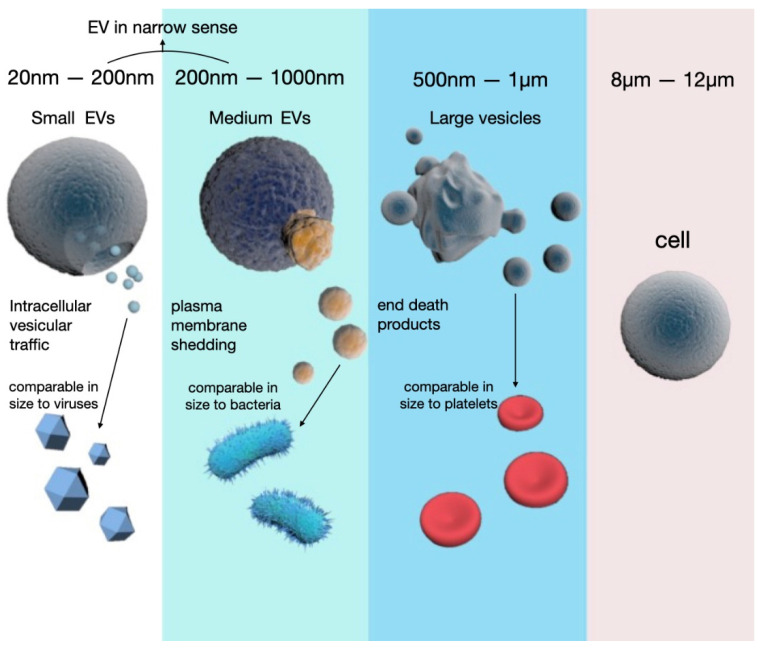
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of extracellular vesicle size and biogenesis. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) refer to a group of heterogeneous vesicles ranging from 20 nm to 5 μm. Small vesicles ranging from 20 to 200 nm used to be named exosomes, while small to medium-size vesicles ranging from 200 to 500 nm used to be called microvesicles (MVs). The largest EVs, which used to be called apoptotic bodies (ABs), are often generated from dying cells. The biogenesis of these EVs has distinct pathways. As illustrated here, small EVs are often generated via a long journey including endosomes, ER/Golgi, and multivesicular bodies (MVBs). On the other hand, the other larger EVs can be produced via direct budding from the plasma membrane. It is commonly facilitated by lipid raft proteins as discussed in this review. The largest-size EVs, or previously referred to as ABs, are broken down from apoptotic cells.