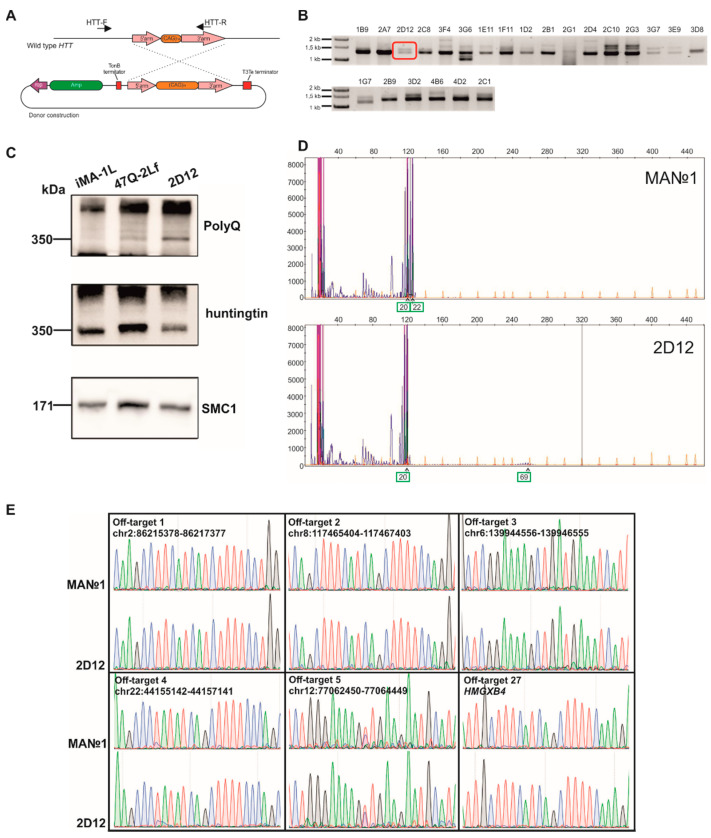
Figure 1.
Generation of human embryonic fibroblast clones harboring the CAG expansion in the first exon of the HTT gene through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homologous recombination: (A) The scheme of homologous recombination between wild-type HTT and the donor construct. HTT-F and HTT-R: primers for the detection of the insertion of the expanded CAG repeat tract into HTT; (B) PCR analysis of HTT allele lengths in the mutant cell clones. The clone selected for further study is highlighted by a red frame; (C) Western blot analysis of HTT expression in the mutant cells; (D) Fragment analysis of PCR products by capillary electrophoresis. Green squares and arrows indicate the number of CAG repeats in the HTT alleles; (E) Sequenograms of the off-target sites in the cell clones’ genomes. CRISPR/Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9).