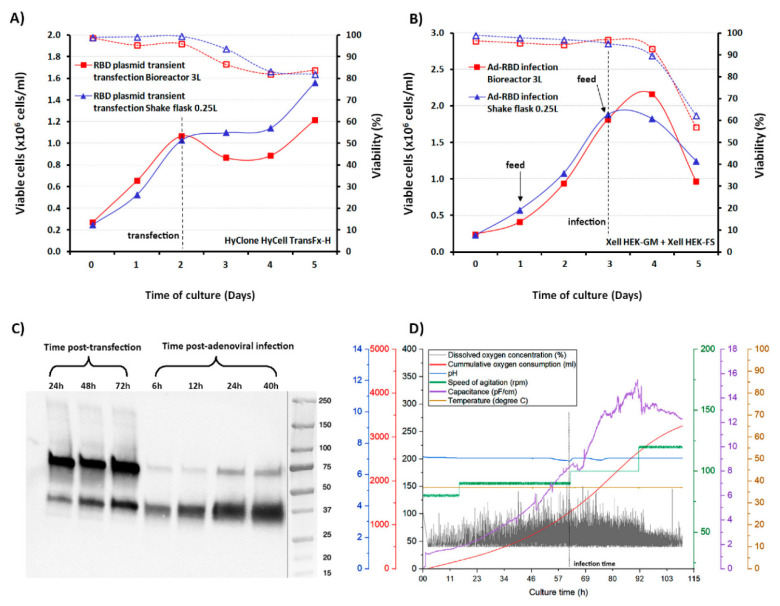
Figure 2.
Characterization of RBD expression kinetics in HEK293SF cells grown at small scale in shake-flask and in 3L bioreactors, following plasmid DNA transient transfection or adenoviral infection. (A) Time course of the viable cell growth and cell viability of HEK293SF cells cultured in batch mode in HyCell TransFx-H medium, transfected with the plasmid pTPA_SP-RBD-His-SrtA at a cell density of 1 × 106 cells/mL at small scale (250 mL shake flasks) and in 3L-Bioreactor. The time of transfection for both cultures is indicated with an arrow. (B) Time course of the viable cell growth and viability of HEK293SF cells in Xell HEK-GM medium for RBD production mediated by Ad-hTPA_SP-RBD-His-SrtA adenovirus infection. The time course of cultures with the same volumes as in (A), operated in fed-batch mode are shown, with the feed supplement (Xell HEK-FS) initiated at a cell concentration of 1 × 106 cells/mL and administered every two days by bolus addition at 5% (v/v) (indicated in the figure with arrows). The infection was set at a cell density of 2 × 106 cells/mL. The cultures were strictly monitored and harvested when the cell viability reached approximately 70%. (C) Time-course expression analysis of the RBD secreted to the culture in the 3L bioreactor productions conducted by transient transfection (24–72 hpt) or adenoviral infection (6–40 hpi) of the cells. The RBD detection was conducted by Western Blot using the polyclonal antibody. (D) In-line measurements and profile of various bioreactor sensors and process parameters from the 3L-RBD production mediated by the adenovirus are shown (speed of agitation, pH, dissolved oxygen concentration, cumulative oxygen, and temperature). In addition, the curve of the capacitance values shows the changes registered after infection as the cells undergo the productive phase, in which expression and secretion of the RBD also occurs. The dotted line indicates the time point of infection.