Figure 5. Enzymatic Acrs that inhibit type V-A CRISPR-Cas systems.
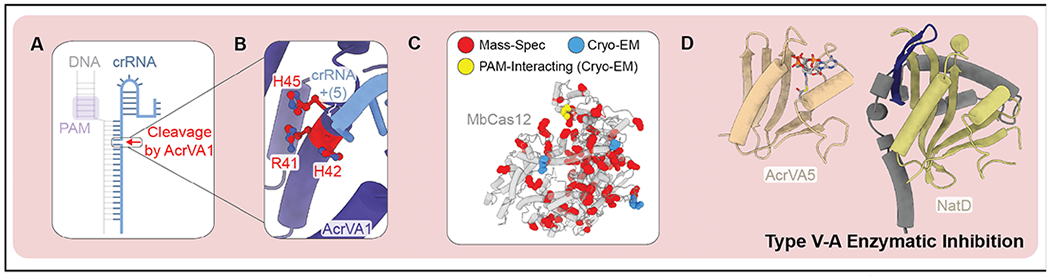
A) AcrVA1 is an endoribonuclease that cleaves between the fifth and sixth position of the crRNA-guide. B) Active site residues of AcrVA1 (red) responsible for crRNA cleavage (PDB: 6NMD). C) Residues of MbCas12 acetylated by AcrVA5 according to mass spectrometry (red) or cryo-EM and mass spec (blue and yellow) (PDB: 6IV6). D) Comparison of AcrVA5 (tan) and closest structural homolog (NatD from Homo sapien) (RMSD = 0.82 Å for 36 equivalently positioned C-alpha atoms). Structural features of NatD shared with AcrVA5 colored in olive. Two NatD β-strands that determine acceptor substrate specificity (dark blue) and additional N-terminal structural features (grey) (PDB: 6IUF, 4U9W).
