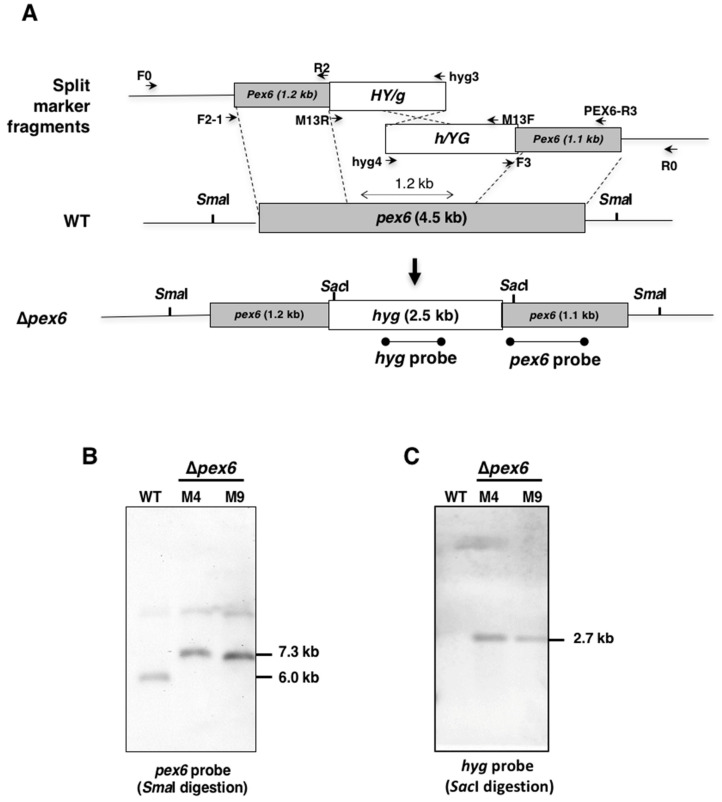
Figure 1.
Deletion of a peroxin 6-coding gene (pex6) using a split marker approach in the tangerine pathotype of A. alternata. (A) Schematic depiction of gene disruption of pex6 via a homologous recombination using truncated but overlapping DNA fragments of a hygromycin phosphotransferase-coding gene (hyg) under control by the Aspergillus nidulans trpC promoter and terminator. Split marker fragments, 5’pex6::5’HY/g fragment and 3’pex6::3’h/YG fusion fragment, were amplified with primers F2-1 pairing with hyg3 and PEX-R3 pairing with hyg4, respectively. Oligonucleotide primers used to amplify each fragment are indicated; (B) Southern-blot hybridization of genomic DNA prepared from wild-type (WT) and two putative pex6 mutants (Δpex6-M4 and M9), in which a 1.2-kb region of pex6 ORF was replaced with a hyg cassette. Fungal DNA was cleaved with SmaI endonuclease, electrophoresed, blotted to a nylon membrane, and hybridized with a pex6 probe. A faint band (estimated > 10 kb), likely due to incomplete digestion, was detected in all three samples; (C) Southern-blot hybridization of genomic DNA digested with SacI and hybridized with a hyg probe.