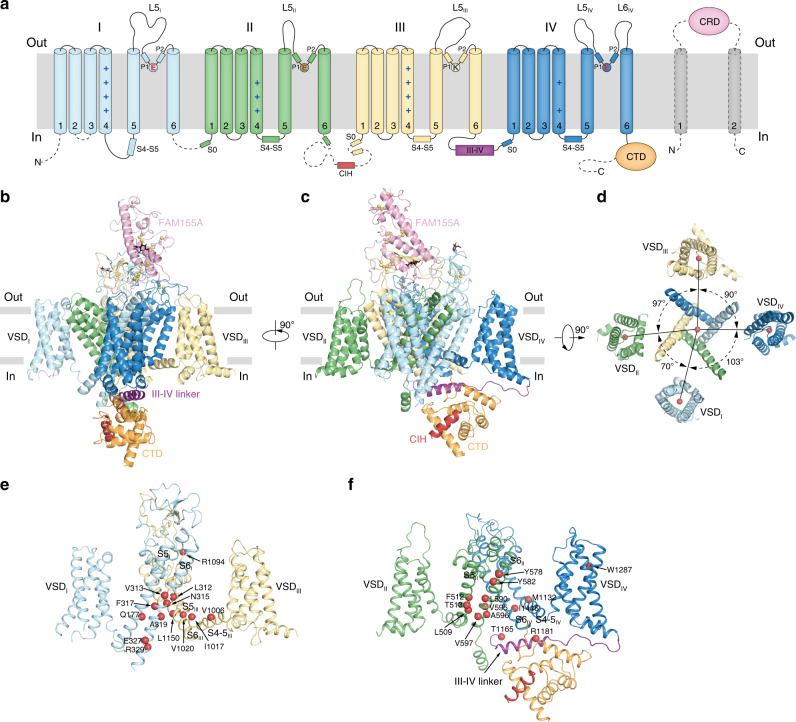
Fig. 1. Overall structure of NALCN and FAM155A complex.
a Topology of NALCN and FAM155A subunits. Helices are shown as cylinders, unmodeled disordered regions are shown as dashed lines. The phospholipid bilayer is shown as gray layers. CTD C-terminal intracellular domain of NALCN. CIH CTD interacting helix of NALCN. CRD cysteine-rich domain of FAM155A. Plus signs represent positively charged residues on S4 segments. Key residues on the predicted selectivity filter are indicated. b Side view of NALCN and FAM155A complex. Sugar moieties are shown as black sticks, side chains of cysteine residues participating in disulfide bond formation are shown as spheres. Sulfur atoms of disulfide bonds were colored in gold and Cα and Cβ atoms were colored the same as each domain. The approximate boundaries of phospholipid bilayer are indicated as gray thick lines. c A 90° rotated view compared to b. d The arrangement of the NALCN transmembrane domain illustrated in the top view. For clarity, only voltage sensors and S6 segments are shown. The angles between adjacent voltage sensors are labeled. Angular measurements were based on the center of mass positions (red spheres) of each domain. e, f Structural mapping of disease-related mutations in NALCN. For clarity, only two nonadjacent domains are shown in each panel. The Cα atoms of disease-related residues are shown as red spheres.