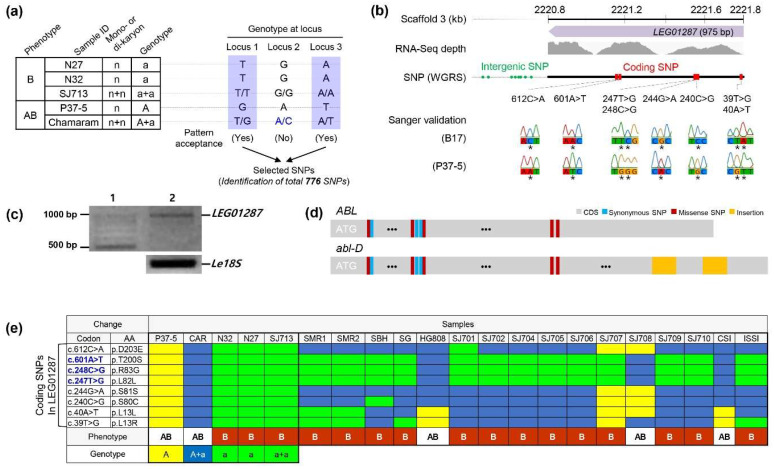
Figure 2.
Identification of a dominant abl-D allele associated with abnormal brown film formation. (a) Identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) through comparison of genome sequences from selected strains. A total of 776 SNPs that the allele combination of genotypes “A” and “a” at each loci met the phenotype pattern (A or AB) were identified. The purple-color shaded boxes indicate an allele that is accepted as a valid SNP. (b) Schematic structure of the candidate gene responsible for abnormal brown film formation with the locations of predicted SNPs indicated. The symbol * means SNP position. (c) RT-PCR analysis of LEG01287 gene expression. Le18 S was used as an internal control. Lane 1—1 Kb molecular weight marker; Lane 2—Le18 S and LEG01287 PCR products. (d) Schematic diagram of ABL (wild-type, upper) and abl-D (mutant type, lower). Polymorphism locations are indicated. The orange-color boxes indicate insertions of the abl-D allele. (e) Identification of the most relevant trait-associated SNPs. CAR, Chamaram; SJ713, Sanjo713; SMR1, Sanmaru1; SMR2, Sanmaru2; SBH, Sanbaekhyang; SG, Songgo; SJ701, Sanjo701; SJ702, Sanjo702; SJ704, Sanjo704; SJ705, Sanjo705; SJ706, Sanjo706; SJ707, Sanjo707; SJ708, Sanjo708; SJ709, Sanjo709; SJ710, Sanjo710; CSI, Chamsongi; and ISSI, Iseulsongi. Polymorphisms of ABL are represented by yellow for dominant genotype “A” (i.e., P37-5); blue for heterozygous dominant genotype “A + a’” (i.e., CAR); green for recessive genotypes “a” (i.e., N32 and N27) or “a + a” (i.e., SJ713), identical to B17 (reference) alleles. Mycelial film phenotypes are indicated as brown (B) and abnormal brown (AB).