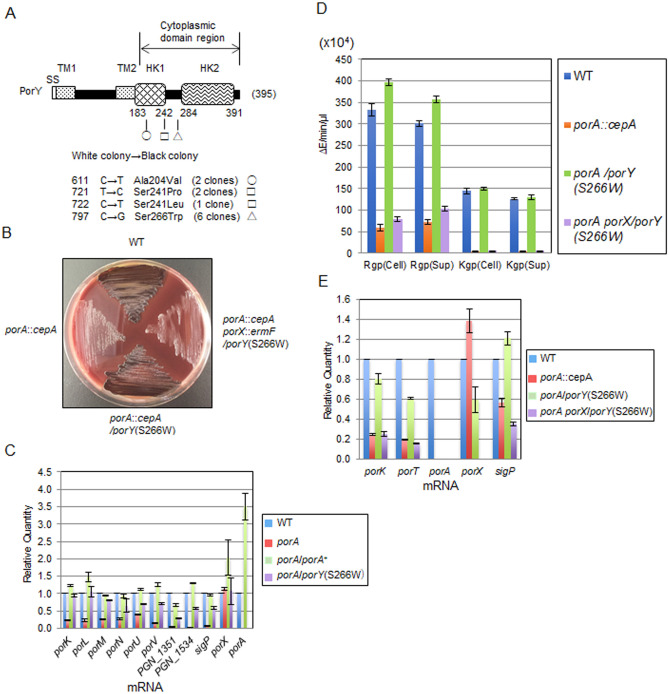
Figure 2.
Pseudo-revertants from the porA deletion mutant. (A) Mutations in porY of the pseudo-revertants. Mutations causing amino acid substitutions were found in the cytoplasmic domain-encoding region of porY. HK, histidine kinase domain; SS, signal sequence; TM, transmembrane region. Circle, square, and triangle indicate amino acid substitutions at 204, 241, and 266, respectively. (B) Colony pigmentation of the wild type, ΔporA, ΔporA/porY(S266W), and ΔporA ΔporX/porY(S266W) strains on the blood agar plate for 6 days. (C) qRT-PCR expression analysis of various T9SS-related genes in the wild type, ΔporA, ΔporA/porA+ and ΔporA/porY(S266W) strains. The mean of expression of each wild type gene was regarded as 1. (D) Gingipain activities of the wild type, ΔporA, ΔporA/porY(S266W), and ΔporA ΔporX/porY(S266W) strains. (E) Expression of the porK, porT, porA, porX, and sigP genes in the wild type, ΔporA, ΔporA/porY(S266W), and ΔporA ΔporX/porY(S266W) strains. RNA samples of the strains were subjected to qRT-PCR analysis. The mean expression of each wild type gene was regarded as 1.