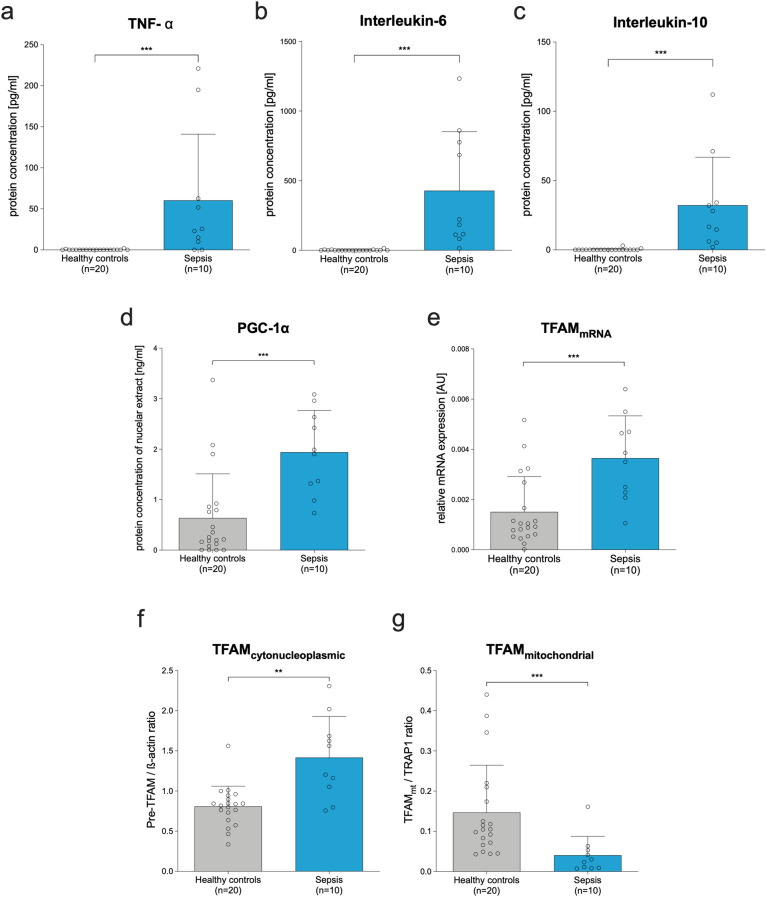
Figure 1.
Sepsis is associated with increased extramitochondrial but diminished intramitochondrial TFAM abundance. Results representing PBMCs from sepsis patients (n = 10; blue bars) sampled within 24 h after the diagnosis of sepsis compared to healthy controls (n = 20; grey bars). Upper panel: Concentration of selected cytokines serum of septic patients and healthy controls. (a) TNF-α, (b) Interleukin-6, and (c) Interleukin-10. (d) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) level (ELISA of nuclear protein extracts). (e) Relative TFAM mRNA expression (quantitative polymerase chain reaction; compared to beta actin) of PBMCs; AU: arbitrary units. (f,g) Relative TFAM protein expression in cytonucleoplasm normalized to beta actin (f) and relative intramitochondrial TFAM protein amount normalized to TNF receptor-associated protein 1 (g). Each circle represents an individual volunteer/patient; columns with error bars represent mean and SD. There were no missing data. P-values were determined using the Mann–Whitney test; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Cytokine concentrations pg/mL were derived from a calibration curve. All exact values are presented in the Source Data file.