Fig. 2.
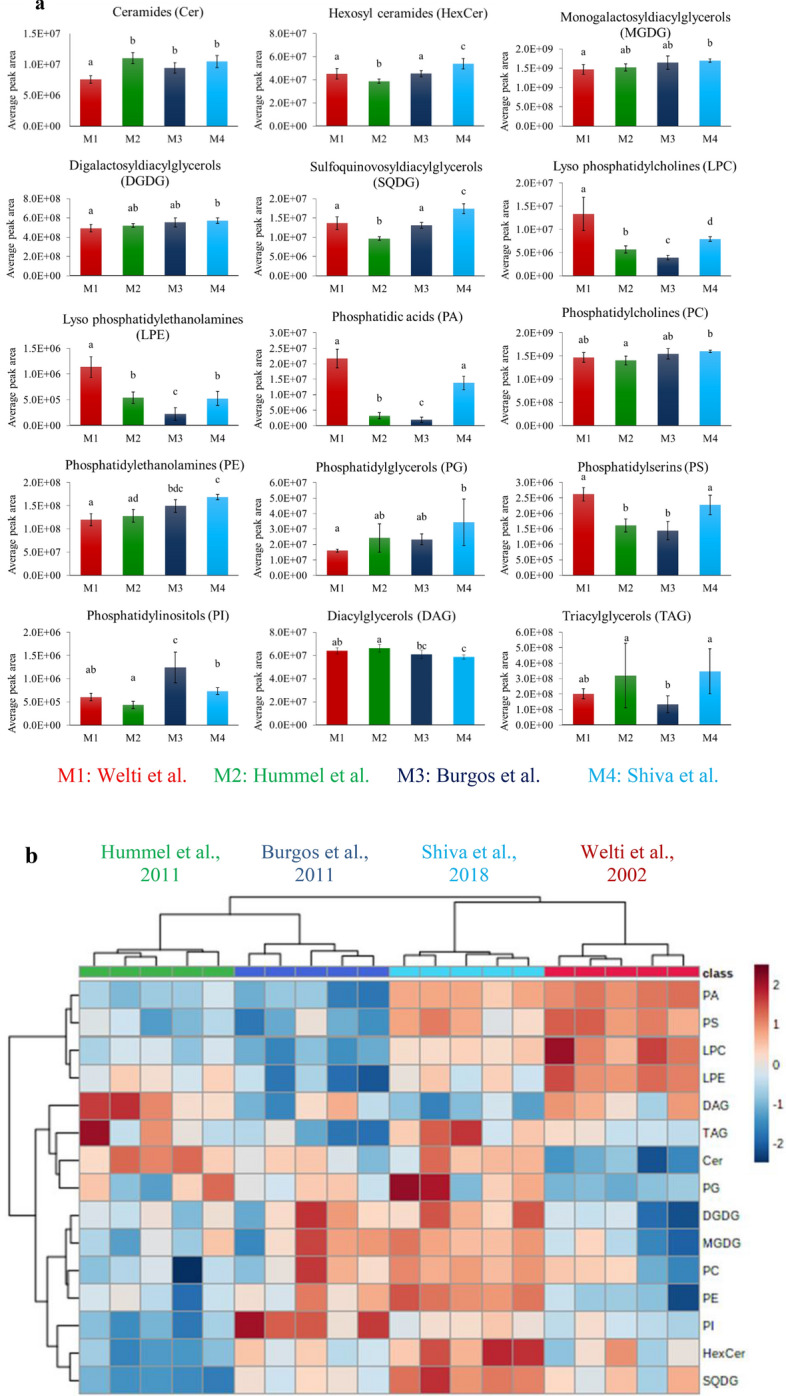
a A comparison of the extractability of individual lipid classes from Arabidopsis leaves using the four different lipid extraction methods. Data consist of 208 annotated lipids following LC–MS data processing through MS-DIAL. Bars show the average peak area of the lipids belonging to a class normalized to the fresh weight of the leaf sample (mean ± SD, n = 5). Different letters above bars of the same tissue indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) as determined by ANOVA and Tukey’s test. The bars in red represent the results obtained from the method of Welti et al. [18], green bars represent results from the method of Hummel et al. [24], dark blue bars represent results from the method of Burgos et al. [27] and light blue colour bars represent the results from the method of Shiva et al. [23]. b. A heat map of the lipid classes identified in leaf extracts (n = 5) when the four protocols were applied M1: Welti et al. [18], M2: Hummel et al. [24], M3: Burgos et al. [27], M4: Shiva et al. [23]
