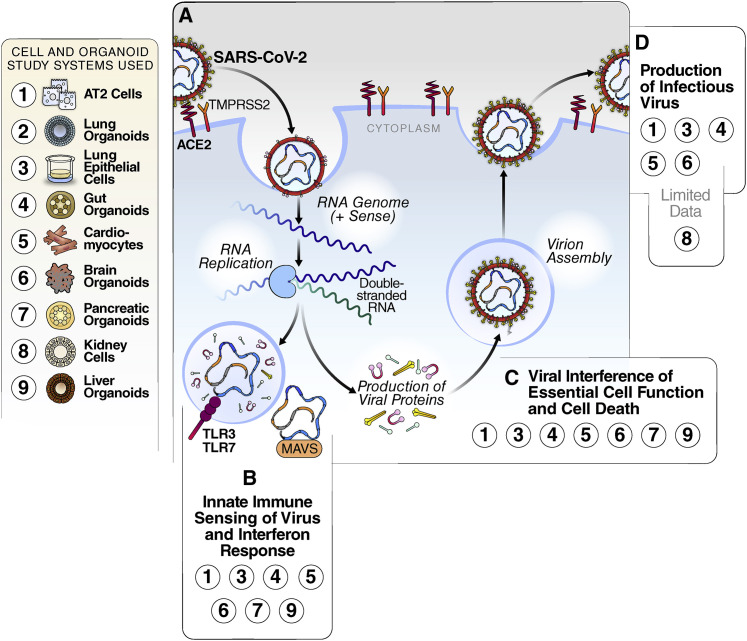
Figure 2.
SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Interaction with Host Cells
(A) Simplified schematic of the viral replication cycle. The virus enters the cell through binding of the ACE2 receptor and is internalized. Inside of the cell, viral RNA is produced, and structural and non-structural proteins are translated. New virions are assembled and released from the cell, resulting in cell lysis.
(B) Interferon pathway activation by SARS-CoV-2. Innate immune sensors recognize the virus, and transcription of interferon is turned on, leading to the production of interferon-stimulated genes. Stem-cell-derived models in which this has been detected are highlighted in the box.
(C) Disruption of cellular processes by SARS-CoV-2 and cell death. Through the hijacking of host cell proteins and pathways, SARS-CoV-2 can disrupt the essential functions of cells. Stem-cell-derived models in which this has been detected are highlighted in the box.
(D) Viral production. When cells are productively infected, SARS-CoV-2 virions are released at the end of the viral life cycle, causing cell lysis and death. Stem-cell-derived models in which this has been detected are highlighted in the box.