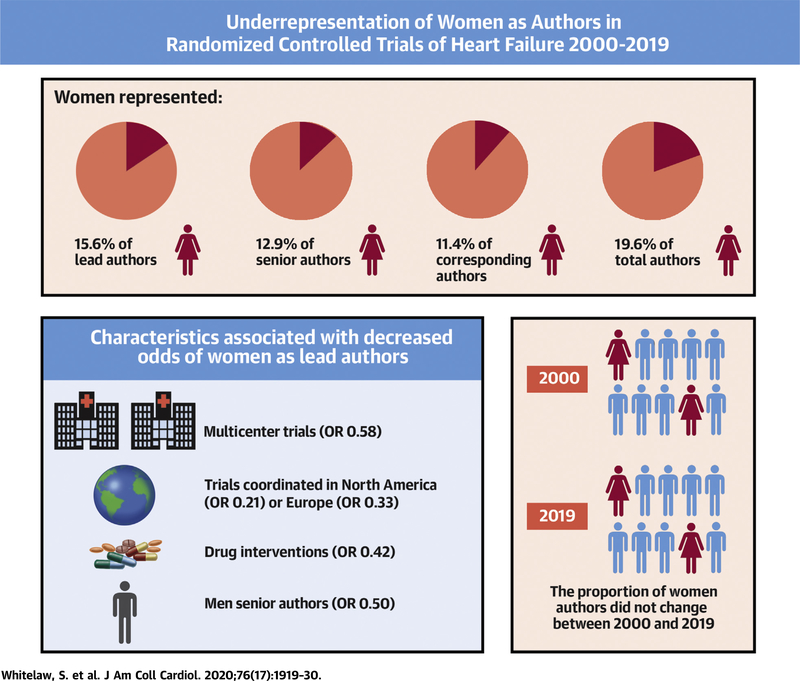
CENTRAL ILLUSTRATION. Under-Representation of Women as Authors in Randomized Controlled Trials of Heart Failure Published in High-Impact Journals.
Of 403 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published in high-impact journals, women were under-represented as authors of heart failure (HF) RCTs, with no change in temporal trends. Women had lower odds of lead authorship in RCTs that were multicenter, coordinated in North America or Europe, tested drug interventions, or had men as senior authors. OR = odds ratio.